Lung Cancer Occurs When Cells Divide In The Lungs Uncontrollably.
06 Apr, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Lung cancer is the third most common Trusted Source cancer and the main cause of cancer-related death in the United States. It is most common in males, and in the U.S., Black males are around 15% more likely to develop it than white males.
Smoking is a major risk factor, though not everyone who develops lung cancer has a history of smoking.
Lung cancer can be fatal, but effective diagnoses and treatments are improving the outlook.
This article will explain what lung cancer is, how to recognize the symptoms, and the treatment options available.
Cancer causes changes in cells that are otherwise healthy. The cells grow too quickly, without dying off.
Normal cells in the body usually die at a certain stage in their life cycle, thereby preventing a buildup of too many cells. In cancer, however, the cells continue to grow and multiply. As a result, tumors develop.
The two main types of lung cancer are small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer, depending on how they appear under a microscope. Non-small cell lung cancer is more common than small cell lung cancer.
Anyone can develop lung cancer, but cigarette smoking and having exposure to smoke, inhaled chemicals, or other toxins can increase the risk.
To discover more evidence-based information and resources for healthy aging, visit our dedicated hub.
The main types of lung cancer are non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. They differ in the size of cell, as seen under a microscope.
Non-small cell lung cancer
Around 84% of lung cancer cases in the U.S. are non-small cell. There are three subtypes:
- adenocarcinoma
- squamous cell cancer
- large cell carcinoma
Small cell lung cancer
Around 13% of lung cancer cases in the U.S. are small cell. This type tends to grow more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer.
People with lung cancer may not have any symptoms until a later stage. If symptoms do appear, they can resemble those of a respiratory infection.
Some possible symptoms Trusted Source includes:
- changes to a person’s voice, such as hoarseness
- frequent chest infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia
- swelling in the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest
- a lingering cough that may start to get worse
- chest pain
- shortness of breath and wheezing
In time, a person may also experience more severe symptoms, such as:
- severe chest pain
- bone pain and bone fractures
- headaches
- coughing up blood
- blood clots
- appetite loss and weight loss
- fatigue
Learn more about the early signs of lung cancer here.
According to the American Cancer Society, the chances of surviving for 5 years or longer after receiving a diagnosis of lung cancer are as follows.
The percentages reflect the chances of a person surviving with lung cancer compared with the chances of a person surviving without lung cancer.
Non-small cell lung cancer
Localized | 63% |
Regional | 35% |
Distant | 7% |
Overall | 25% |
Small cell lung cancer
Localized | 27% |
Regional | 16% |
Distant | 3% |
Overall | 7% |
Treatment will depend on various factors, including:
- the type of cancer
- the location and stage
- the person’s overall health
- their individual preferences
All the treatment options can have adverse effects. A person should speak with their healthcare professional about the most suitable choice for them, including the pros and cons of each option.
Some treatment options include:
- surgery to remove part or all of a lung
- chemotherapy, which refers to a drug treatment that can kill cancer cells and shrink tumors
- radiation therapy, which uses high energy rays to kill cancerous cells
- radiofrequency ablation, wherein a healthcare professional inserts a thin needle and uses an electric current to destroy cancer cells
- targeted therapy, which targets a specific behavior to prevent tumor growth
- immunotherapy, which helps the body fight cancer cells
- palliative therapy, including pain relief, oxygen therapy, and other help that a person may need to manage their symptoms
A healthcare professional will work with the individual and adjust their treatment plan as their needs change.
Lung cancer can be fatal, but emerging treatments mean that many people now survive and recover from lung cancer, especially if they receive an early diagnosis.
Some factors affecting the likelihood of a positive outcome include:
- a person’s overall health
- their age
- the stage of cancer at diagnosis
- the type of cancer they have
It is not possible to predict exactly how cancer will affect an individual, but a healthcare professional can help a person understand what they may be able to expect by looking at the results of tests and other factors.
Lung cancer is a potentially fatal type of cancer, but people who receive an early diagnosis often have a good chance of survival.
People with a high risk of developing lung cancer may wish to consider undergoing regular screening. This can detect the early signs and allow for treatment before the cancer spreads.
Anyone who has concerns about their risk of lung cancer should talk with their healthcare professional
Recent Posts
Bone Marrow Transplantation in children
Aug 27, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

All you need to know about Childhood Cancers
Aug 26, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Signs of Liver Cancer
May 30, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
CAR T-cell therapy
Mar 01, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Mediastinal tumors
Jun 03, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpg)
Blood Cancer Journal
Apr 29, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Transfusion medicine for RBCs
Apr 18, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Sickle Cell Anemia
Apr 15, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What’s new in cancer immunotherapy?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

What is immunotherapy?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What causes breast cancer?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Who gets breast cancer?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Breast cancer symptoms
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpg)
Types of breast cancer
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Types of invasive breast cancers
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Breast cancer treatment plan
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How to prevent cervical cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What is cervical cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Are there tests for early detection?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Breast cancer risk factors
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Staging and Treatment for oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How to prevent oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Risk factors of oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What is oral cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
The Lymph System of the Breast
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What Is Breast Cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpeg)
Kidney Cancer: Myths & Reality
Nov 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Bone marrow biopsy
Sep 29, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Leukemia
May 28, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
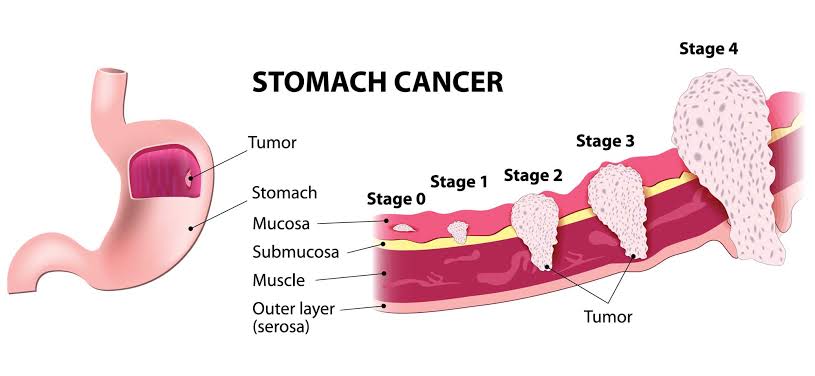
Stomach Cancer
May 28, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
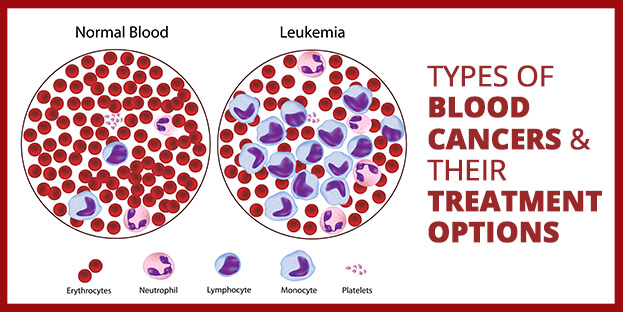
Blood Cancer – Types and Treatment
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
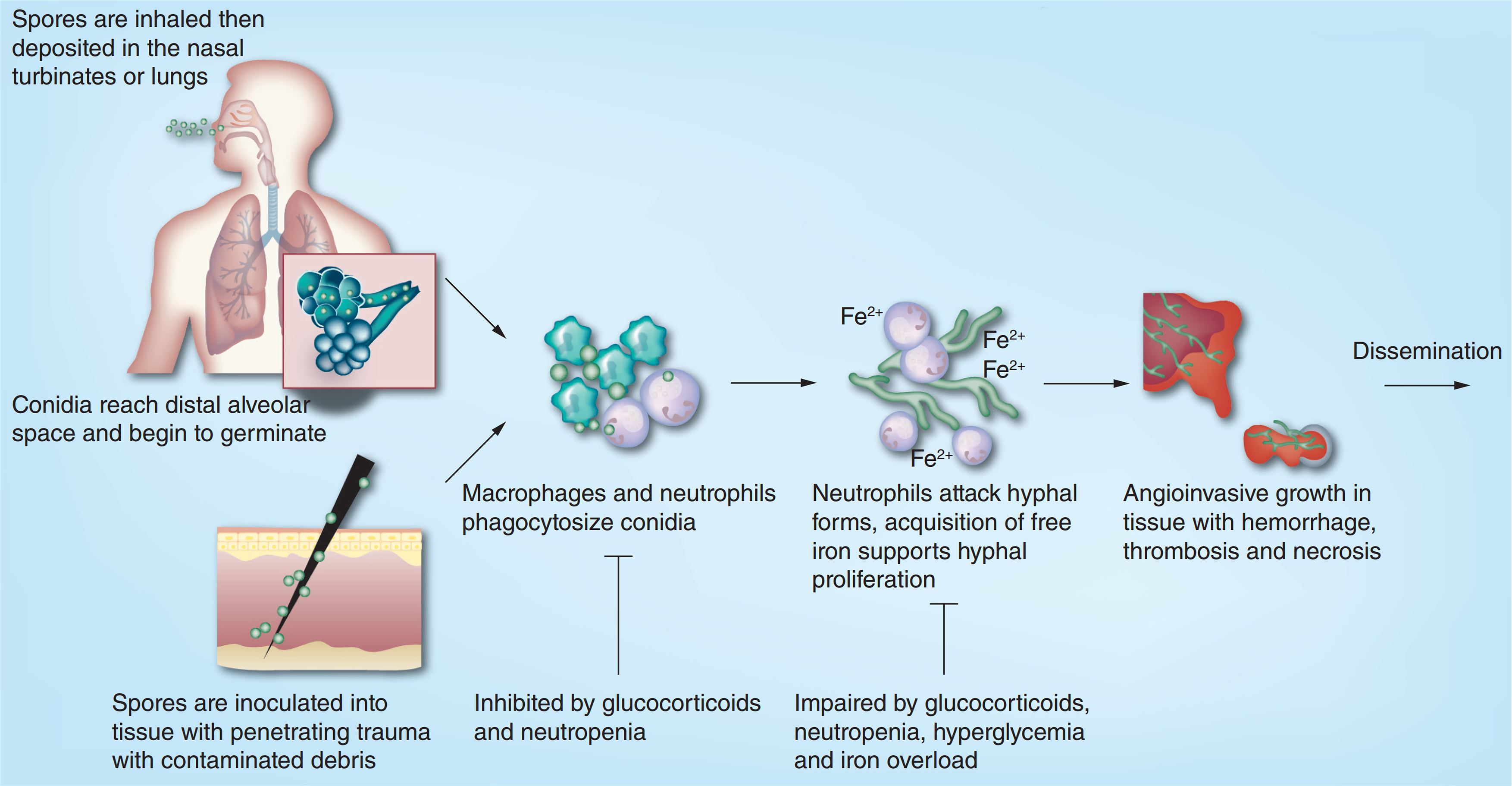
Reasons for mucormycosis in Covid-19
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
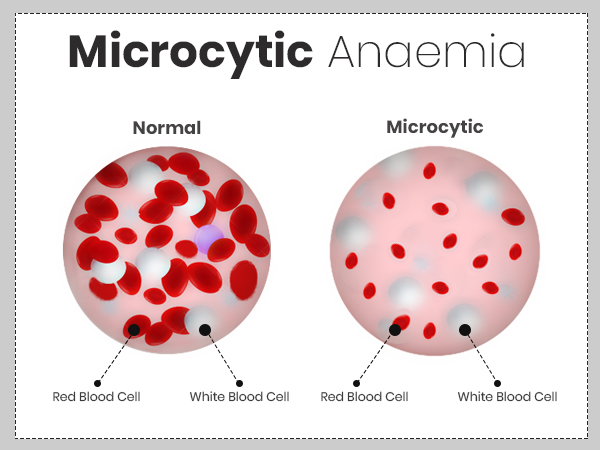
Microcytic and Hypochromic anemia is one of the common scenario we encounter in Clinics
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Updated Recommendations for Breast Cancer Surveillance in Young Female Cancer Survivors
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
vs
May 14, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Risk Factors of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Diagnosing lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
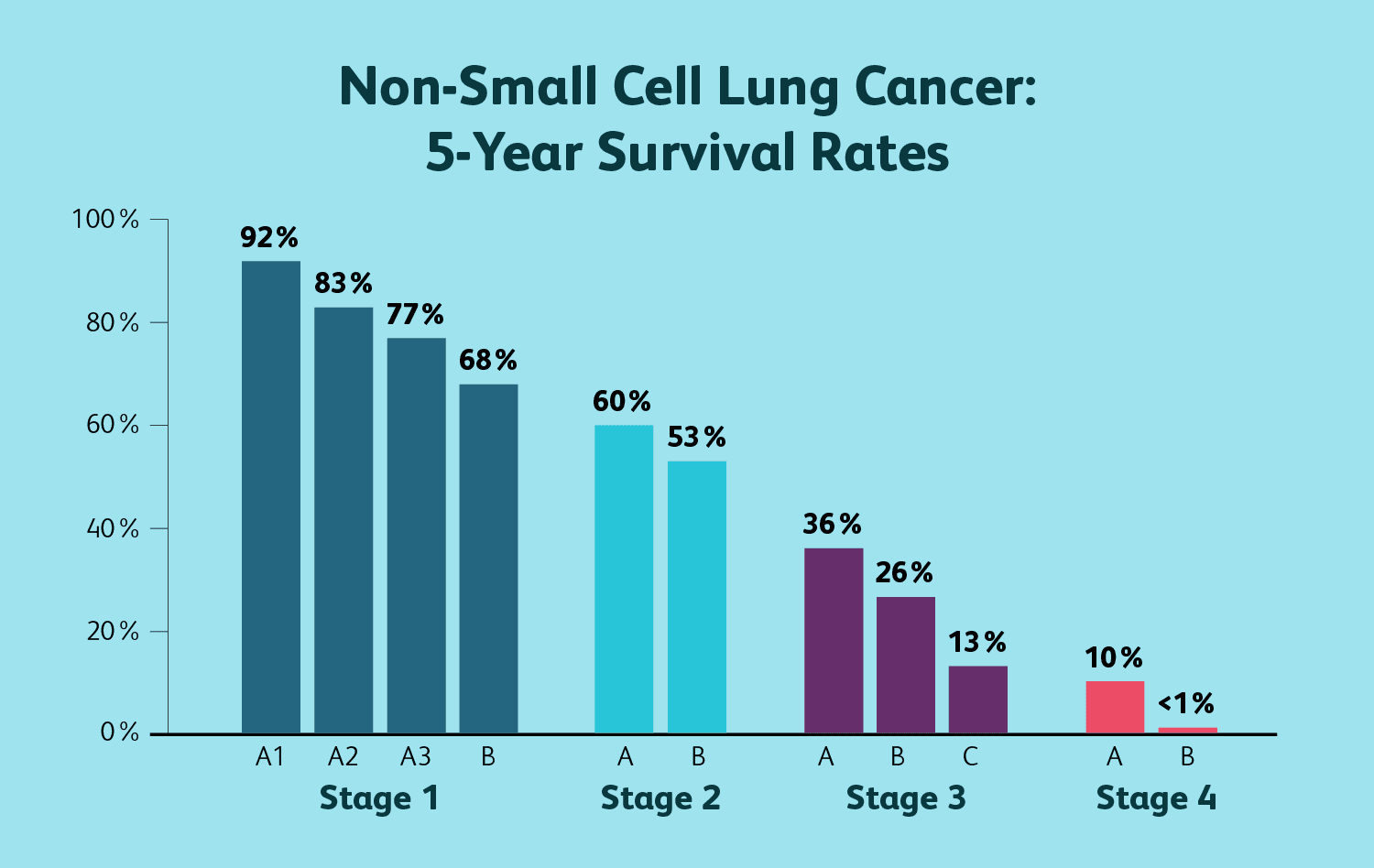
Lung cancer and life expectancy
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Home remedies for lung cancer symptoms
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
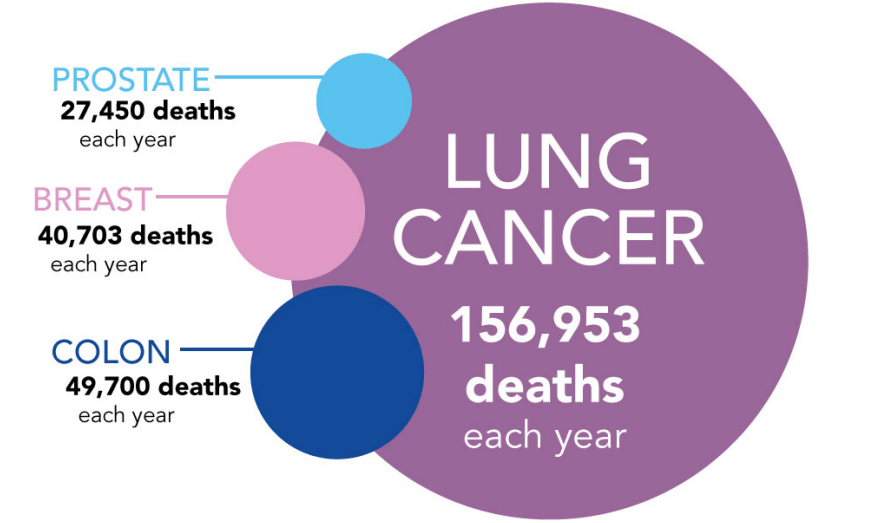
Facts and statistics about lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Diet recommendations for people with lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
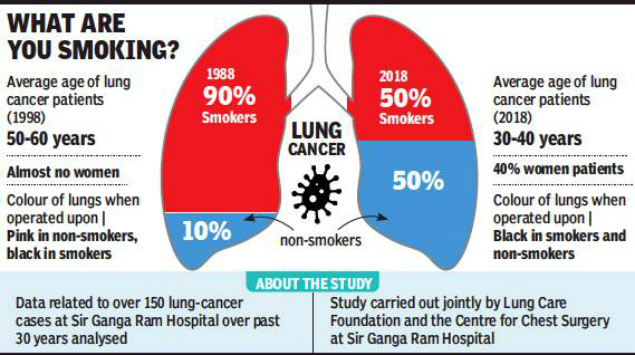
Lung cancer and smoking
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
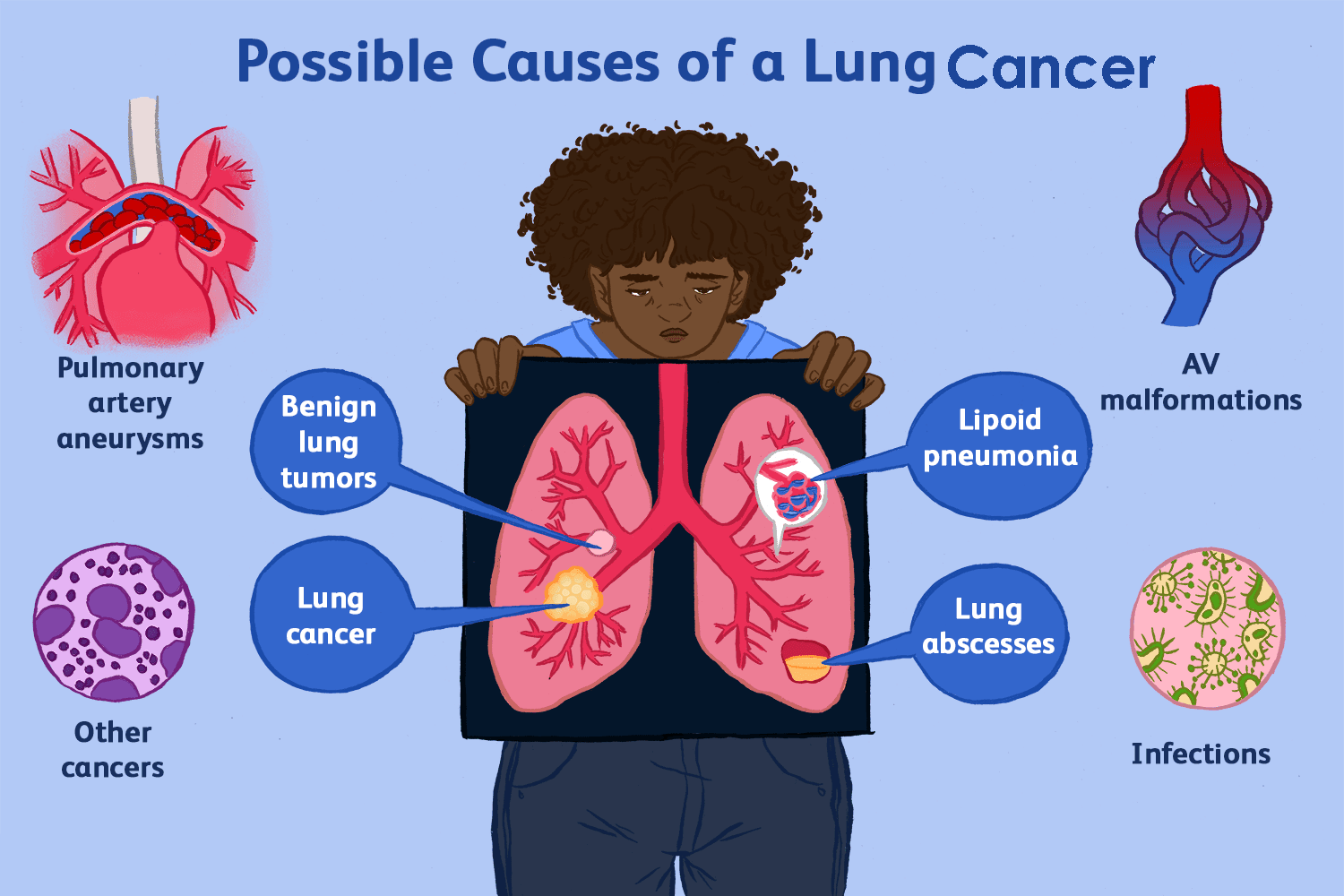
Causes of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
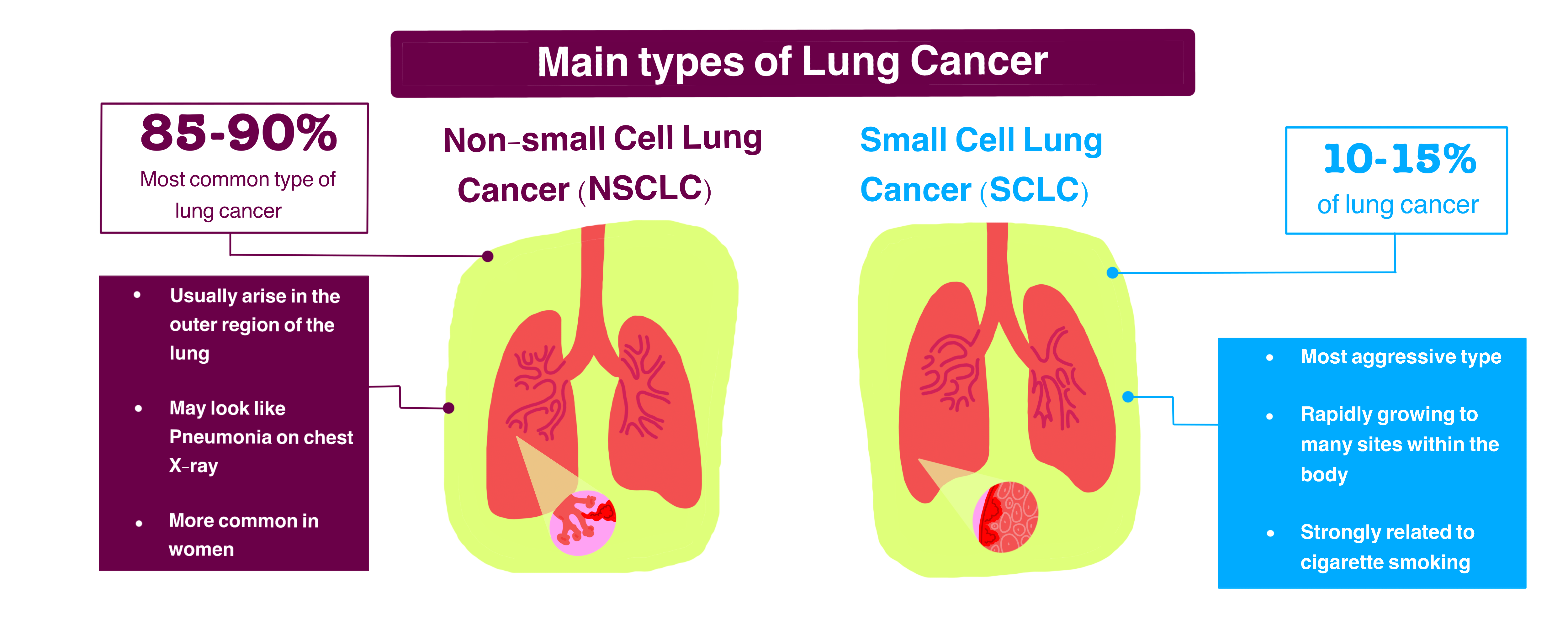
Different Types of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
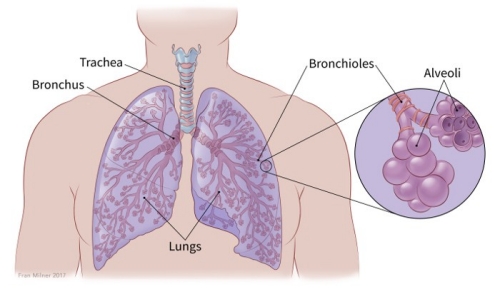
Lung Cancer and its types
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
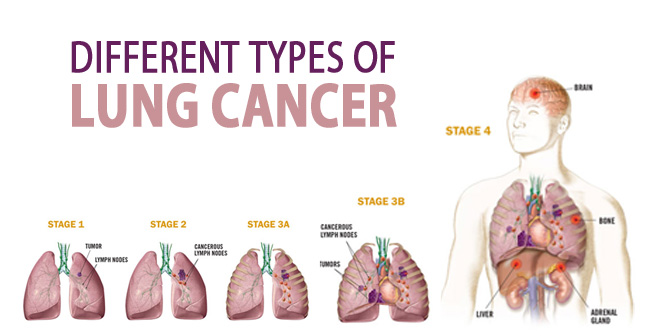
Stages of LUNG CANCER
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
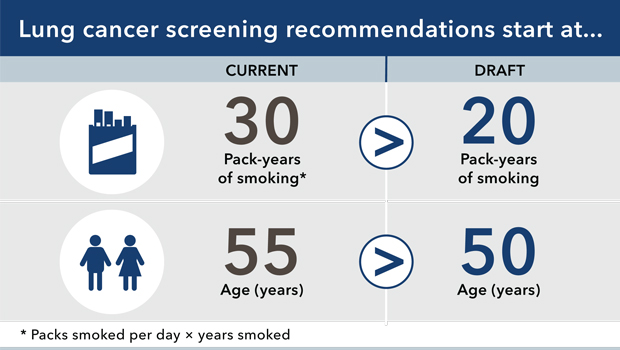
Lung Cancer and Lung Cancer Screening
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
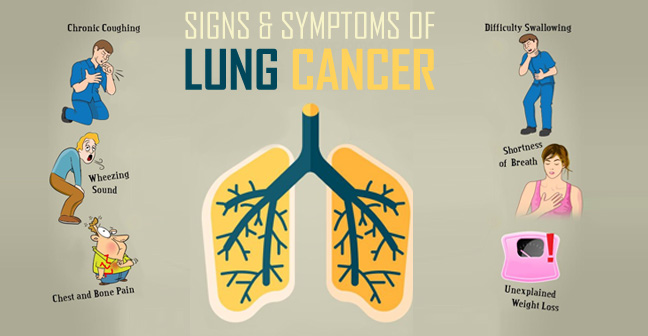
What are the symptoms of lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Lung cancer occurs when cells divide in the lungs uncontrollably.
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

KEYNOTE-365
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
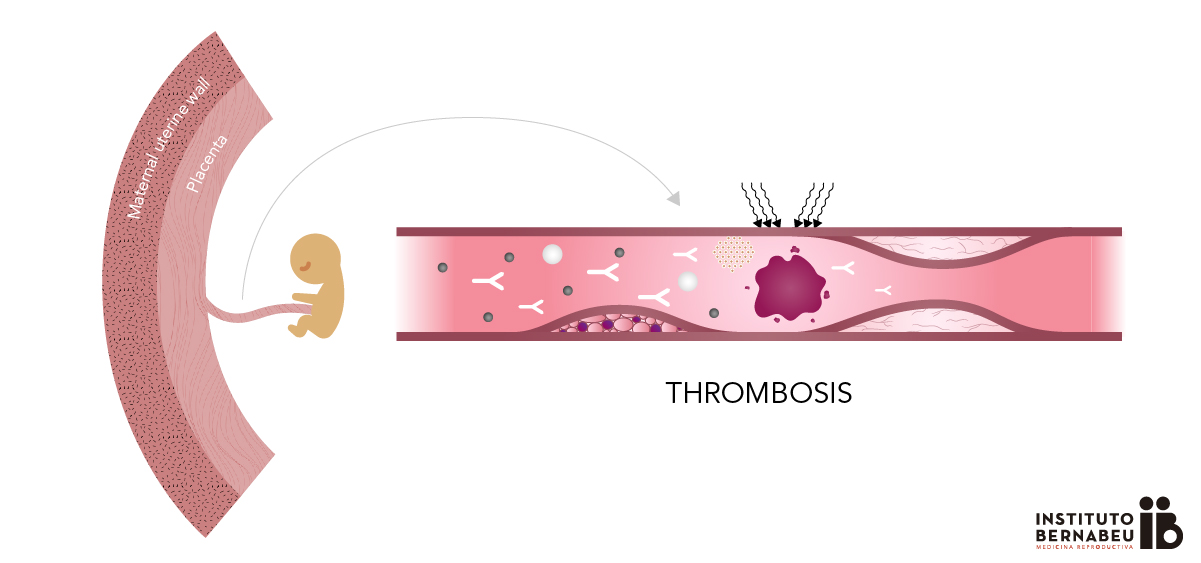
Antiphospholipid syndrome in Pregnancy
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
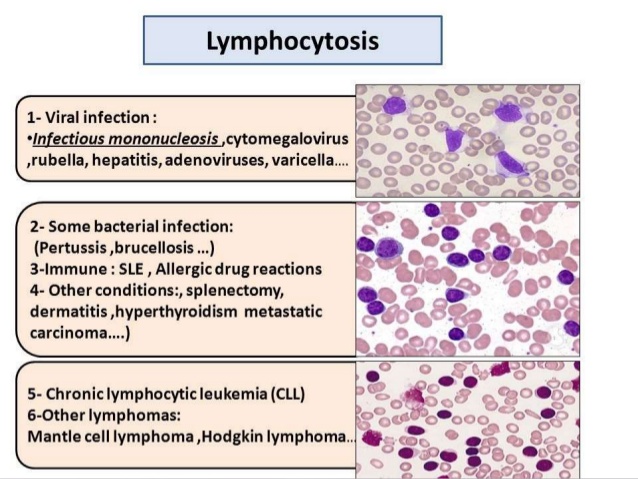
Leucocytosis
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
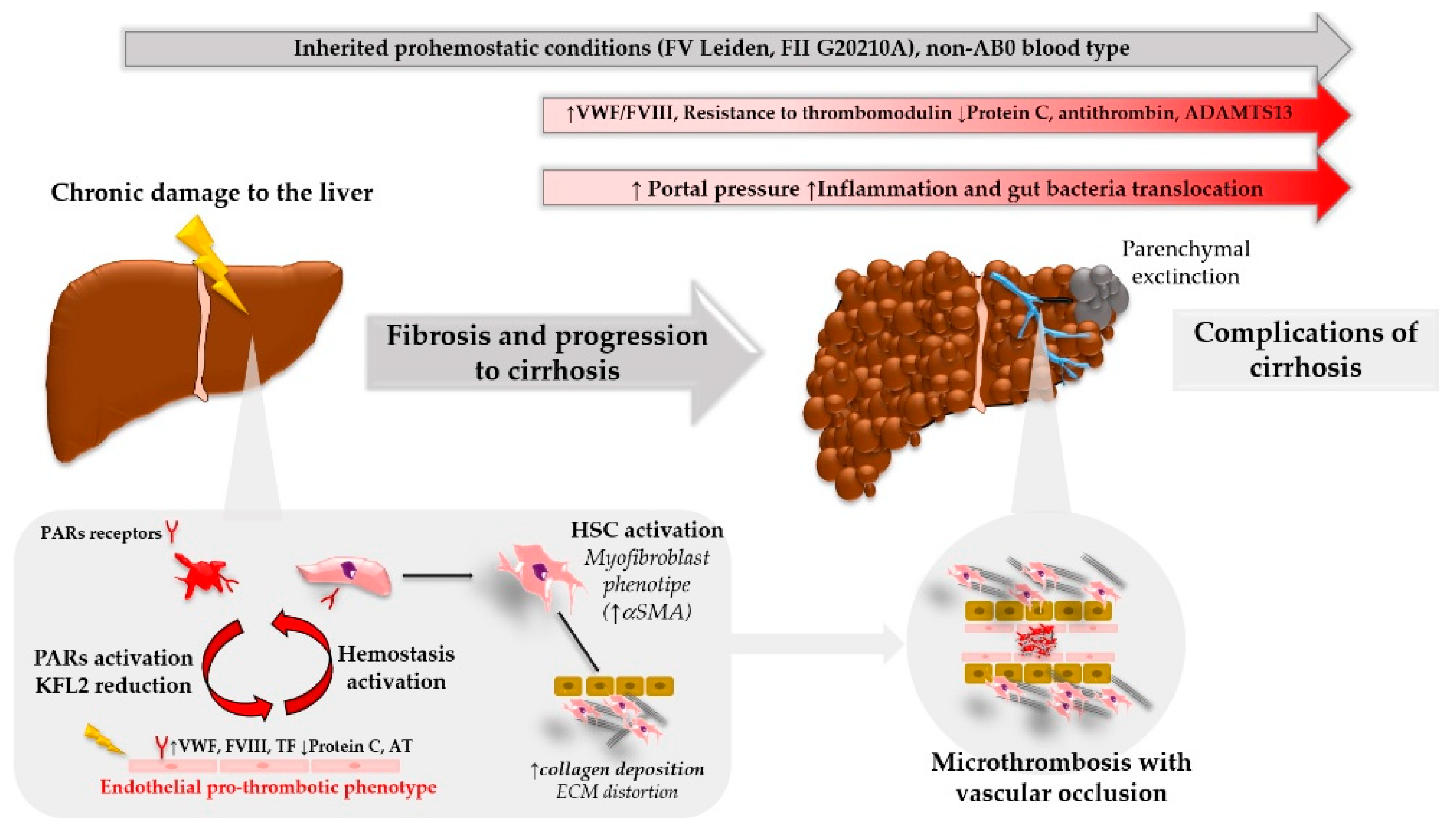
Patients with liver disease often have blood results that give an appearance of a significant bleeding risk
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
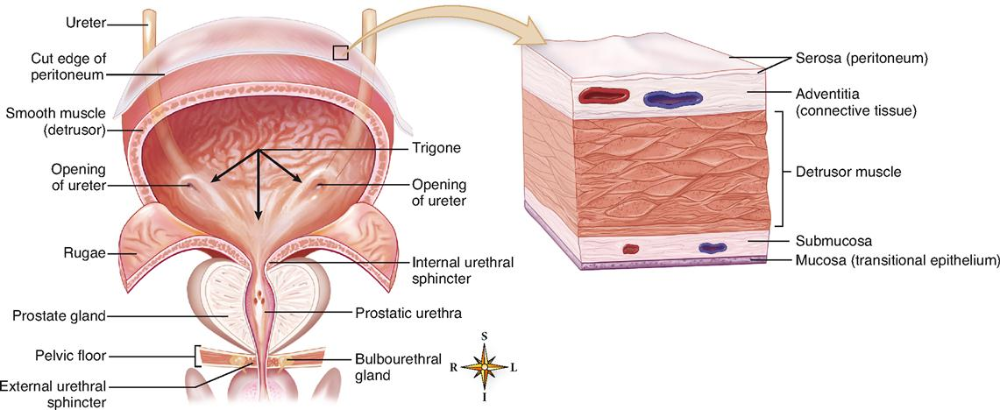
Navigating Uncertain Times in Muscle-Invasive and Advanced Bladder Cancer
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
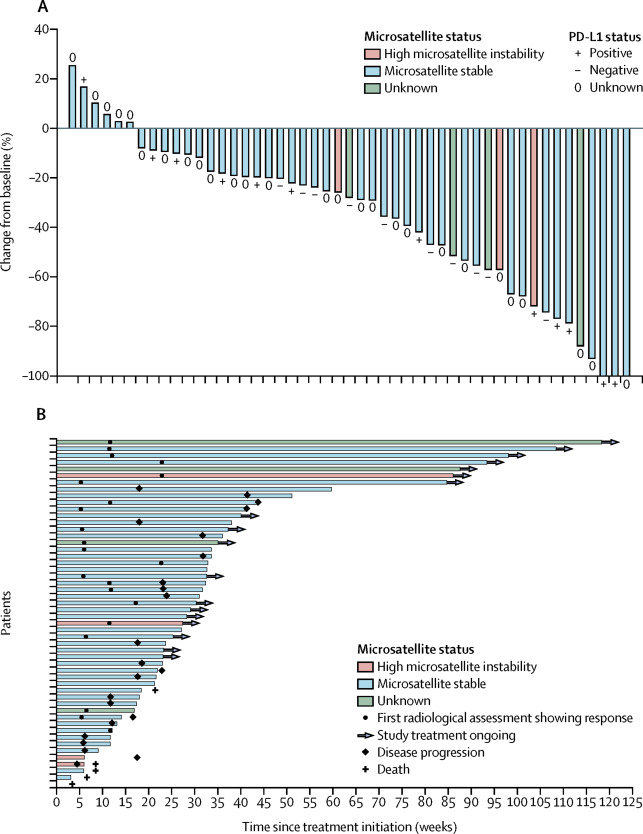
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
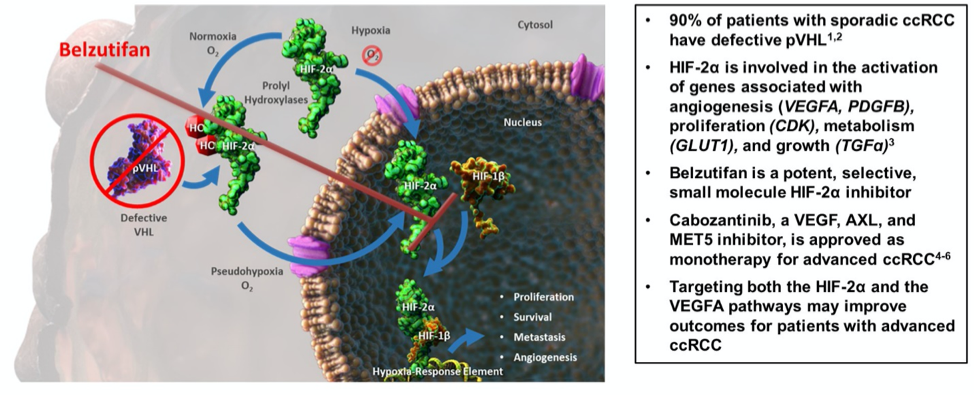
From bench to bedside, another practice-changing treatment is on the road!
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

ASH_hematology VTE guidelines in patients with cancer
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How I Rx Newly Diagnosed Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
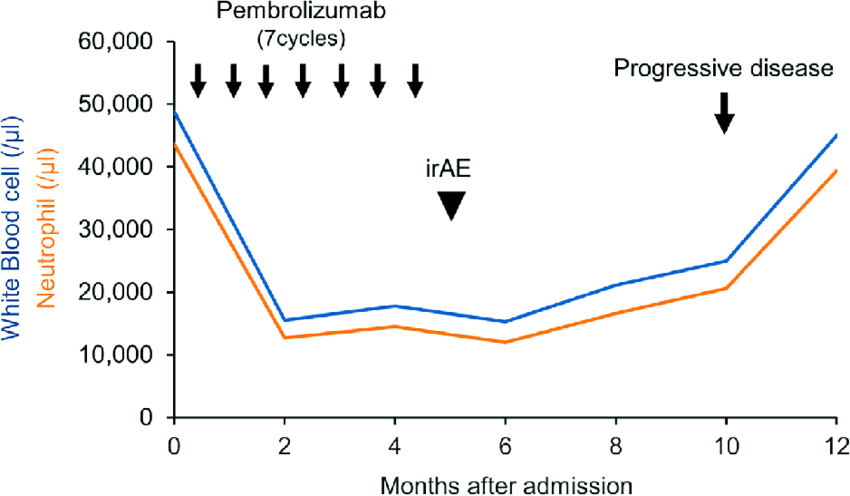
Ipilumumab plus pembrolizumab vs pembrolizumab alone in pdL1 more than 50 percentage Which is better
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
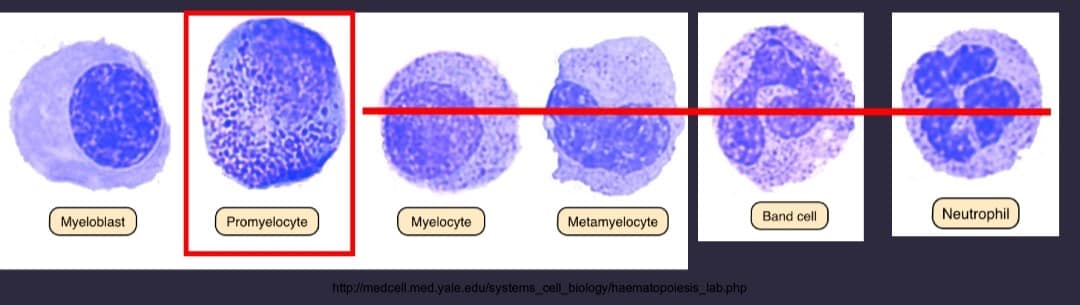
APML is medical emergency
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
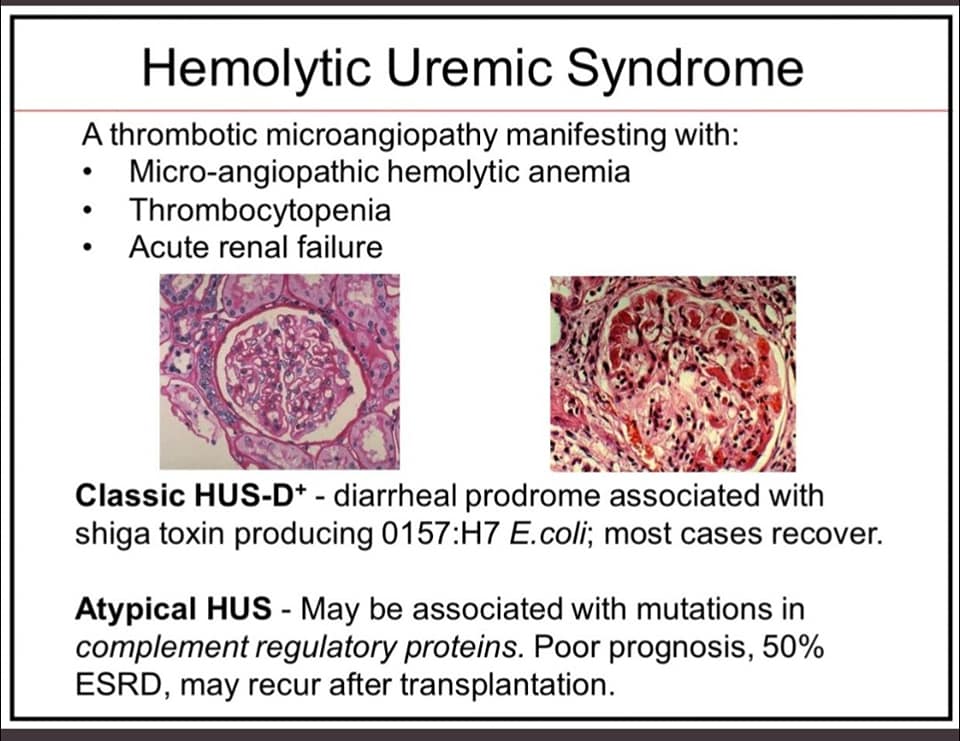
aHUS is a disease of excessive activation of the alternative complement pathway (ACP)
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
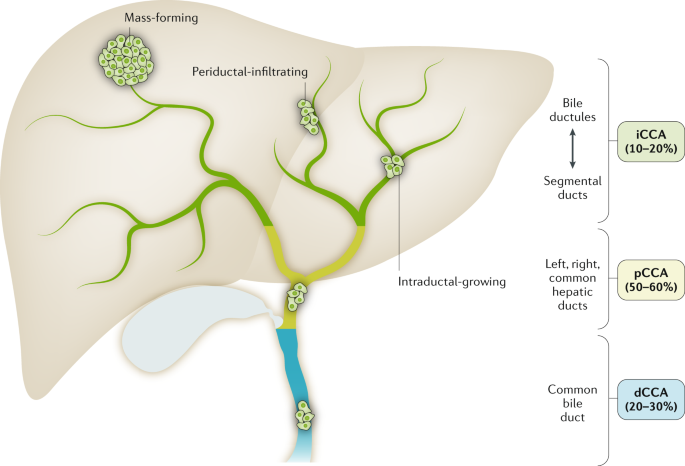
imp. point to reiterate
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
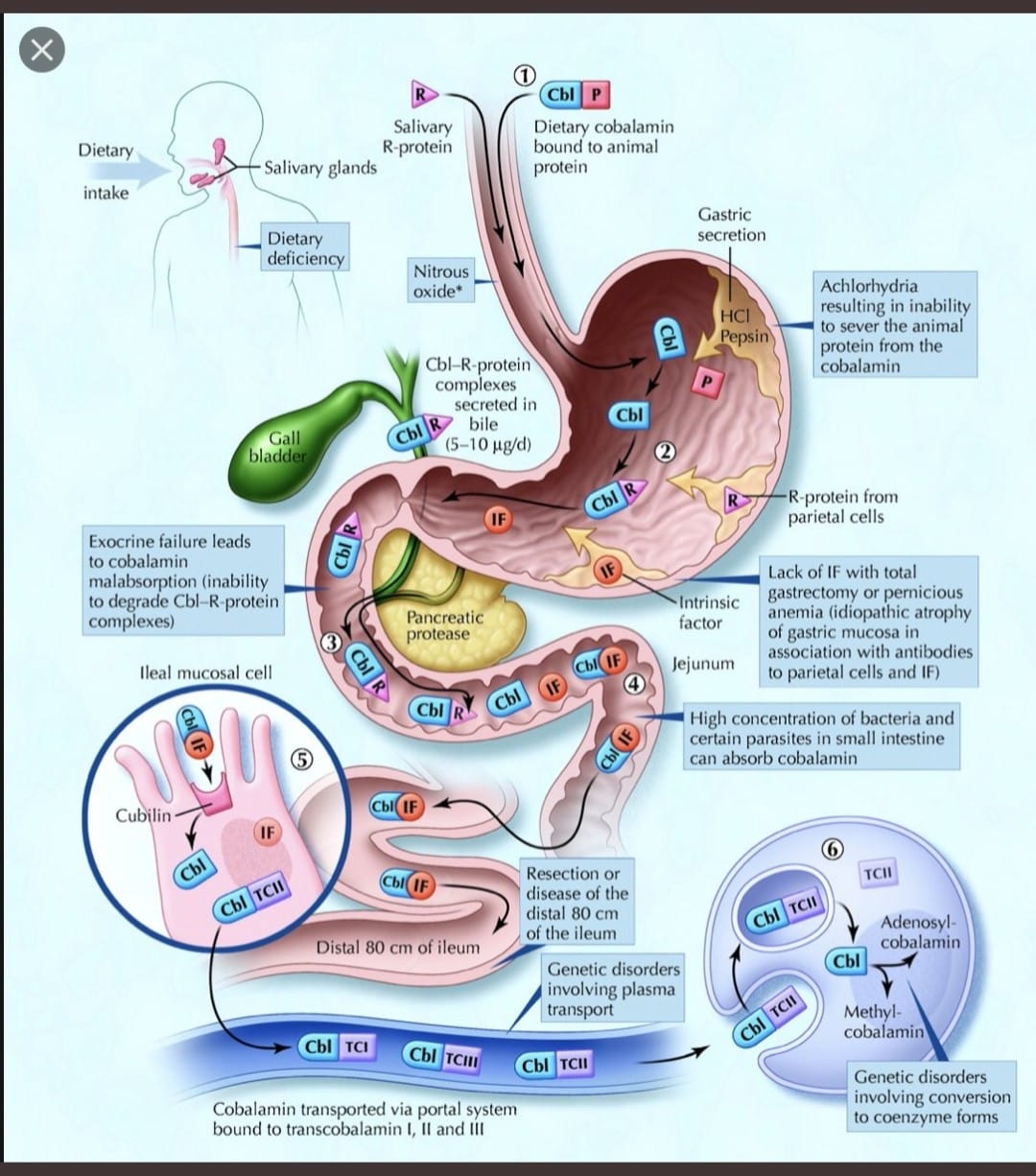
Understand B12 Absorption to Learn B12 Def
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
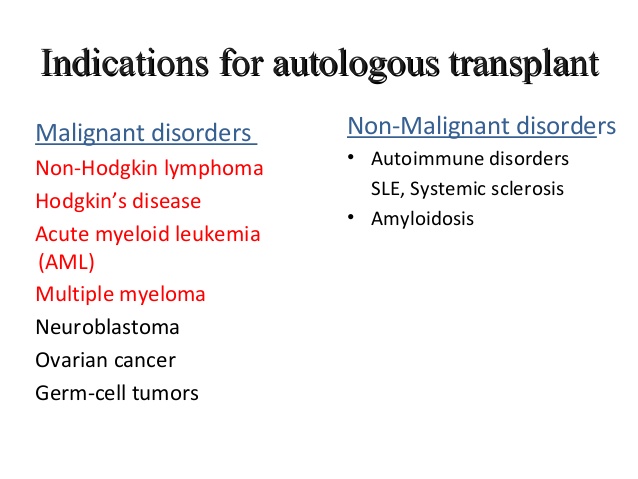
Indications for auto-transplant - for the oncology fellows
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
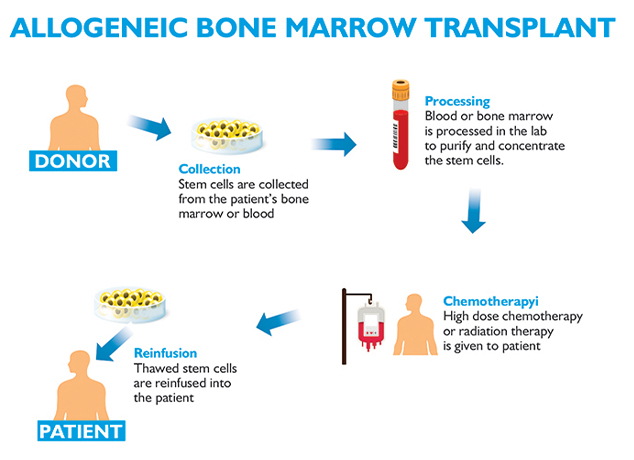
Allogeneic bone marrow transplant is the curative treatment for few relapsed leukemias and Lymphoma
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
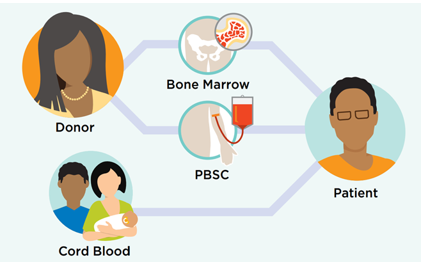
Allo BMT Basics
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
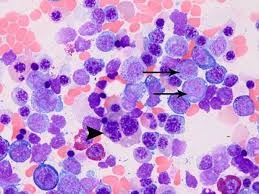
Myeloid HemePath Pearls
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Myeloid HemePath Pearls
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Amyloidosis month
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
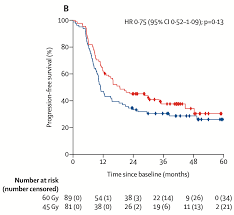
Full publication of randomized Scandinavian dose escalation trial for LS SCLC
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
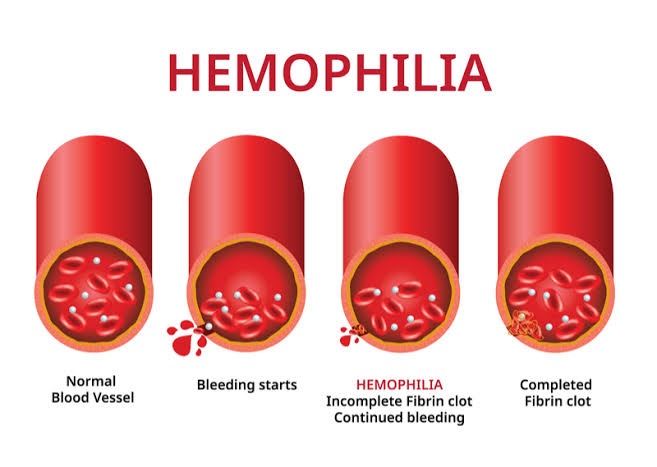
Hemophilia
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Rituximab Maintenance for Follicular lymphoma
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
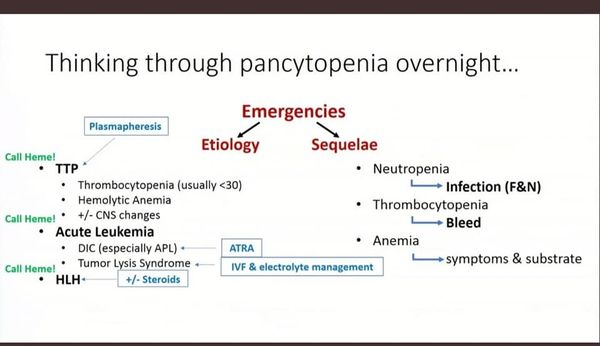
PANCYTOPENIA
Feb 23, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
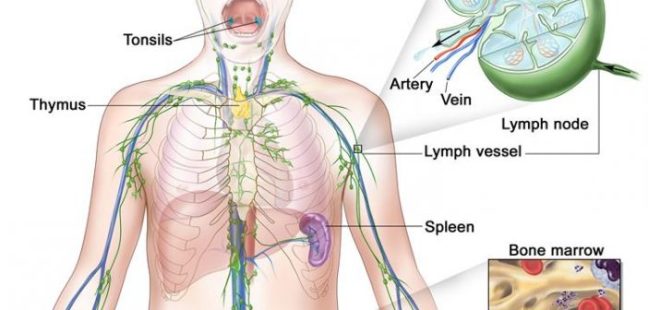
WHAT IS THE MAIN CAUSE OF LYMPHOMA?
Feb 18, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Add a comment