Bone Marrow Transplantation In Children
27 Aug, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is a medical procedure used to treat children with certain types of cancer, blood disorders, and immune system conditions. It involves grafting healthy bone marrow stem cells in place of damaged or sick bone marrow. These stem cells may be obtained by an allogeneic transplant or an autologous transplant from the child's own body.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants:
Autologous Transplant: Prior to therapy, the child's own stem cells are collected and stored. Following high-dose radiation therapy or chemotherapy, the child's body receives the stem cells back.
Allogeneic Stem Cell: Donors of stem cells are often siblings or suitable unrelated donors. When a child's own bone marrow becomes damaged, this kind of transplant is more frequently performed.
What is the process of Bone Marrow Transplant for children?
Diagnosis and Evaluation: The initial step in the bone marrow transplant procedure is a thorough diagnostic and evaluation. This involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient's medical history, a physical examination, and a number of tests to evaluate their general health and verify their transplant eligibility.
Finding a Donor: A eligible bone marrow donor must be found for the transplant to be successful. For young patients, a sibling who is a near match can sometimes be the best choice. Alternative sources, such as unrelated donors or umbilical cord blood units, can be considered if a sibling is not available.
Conditioning: The patient goes through a course of treatment prior to the transplant, which may include radiation therapy, high-dose chemotherapy, or both. In order to make room for the new stem cells to successfully transplant, this procedure helps to destroy any cancer cells that may still be present and suppress the patient's immune system.
Stem Cell Infusion: The actual bone marrow transplant is performed by infusing stem cells. The donor or umbilical cord blood is utilized to extract healthy stem cells, which are then injected intravenously into the patient's bloodstream. After migrating to the bone marrow, these stem cells progressively begin to produce healthy blood cells.
Engraftment and Recovery: The post-transplant period is crucial as the patient's body gets used to the new stem cells. The term "engraftment" describes the transplanted cells' effective implantation in the patient's bone marrow. Patients are continuously watched for infection, graft-versus-host disease, and engraftment throughout this phase (GVHD).
Recent Posts

Bone Marrow Transplantation in children
Aug 27, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

All you need to know about Childhood Cancers
Aug 26, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Signs of Liver Cancer
May 30, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
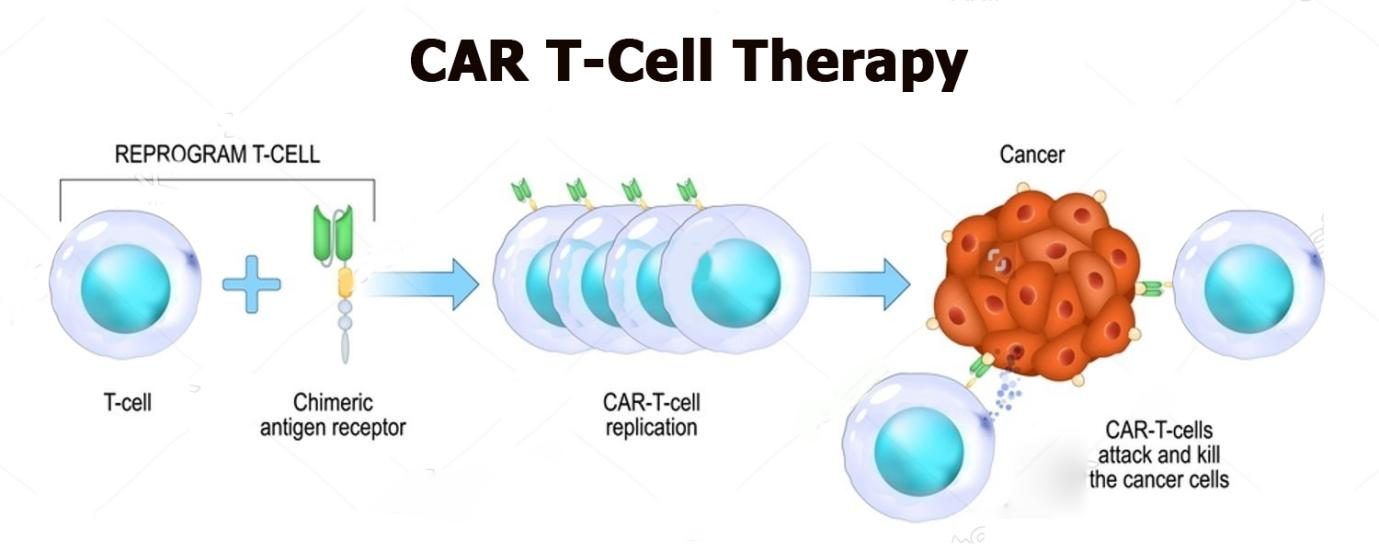
CAR T-cell therapy
Mar 01, 2024
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Mediastinal tumors
Jun 03, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpg)
Blood Cancer Journal
Apr 29, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
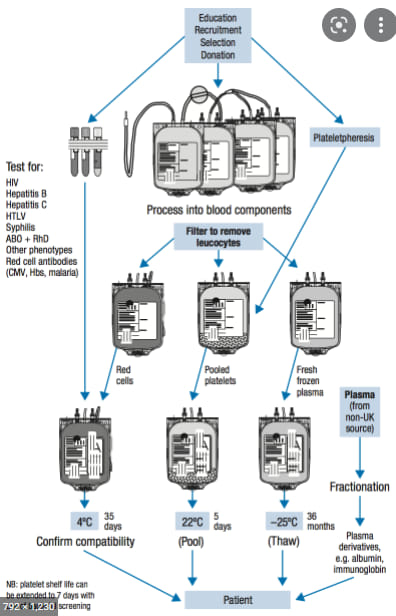
Transfusion medicine for RBCs
Apr 18, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
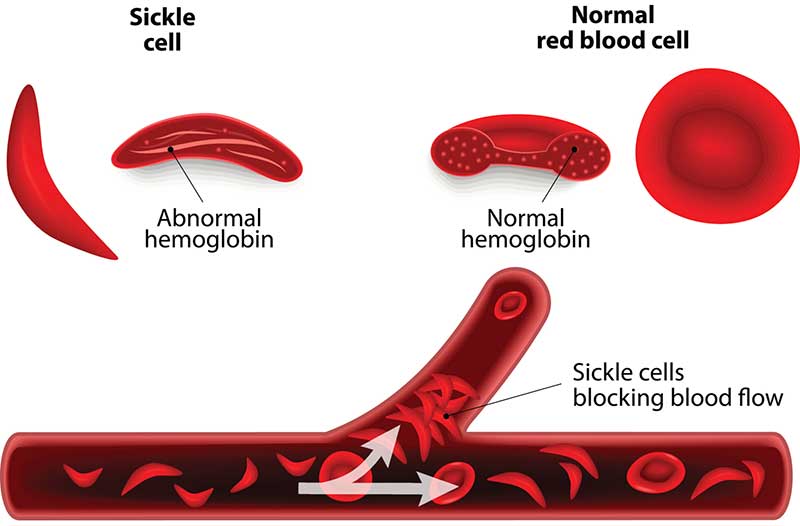
Sickle Cell Anemia
Apr 15, 2022
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What’s new in cancer immunotherapy?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

What is immunotherapy?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
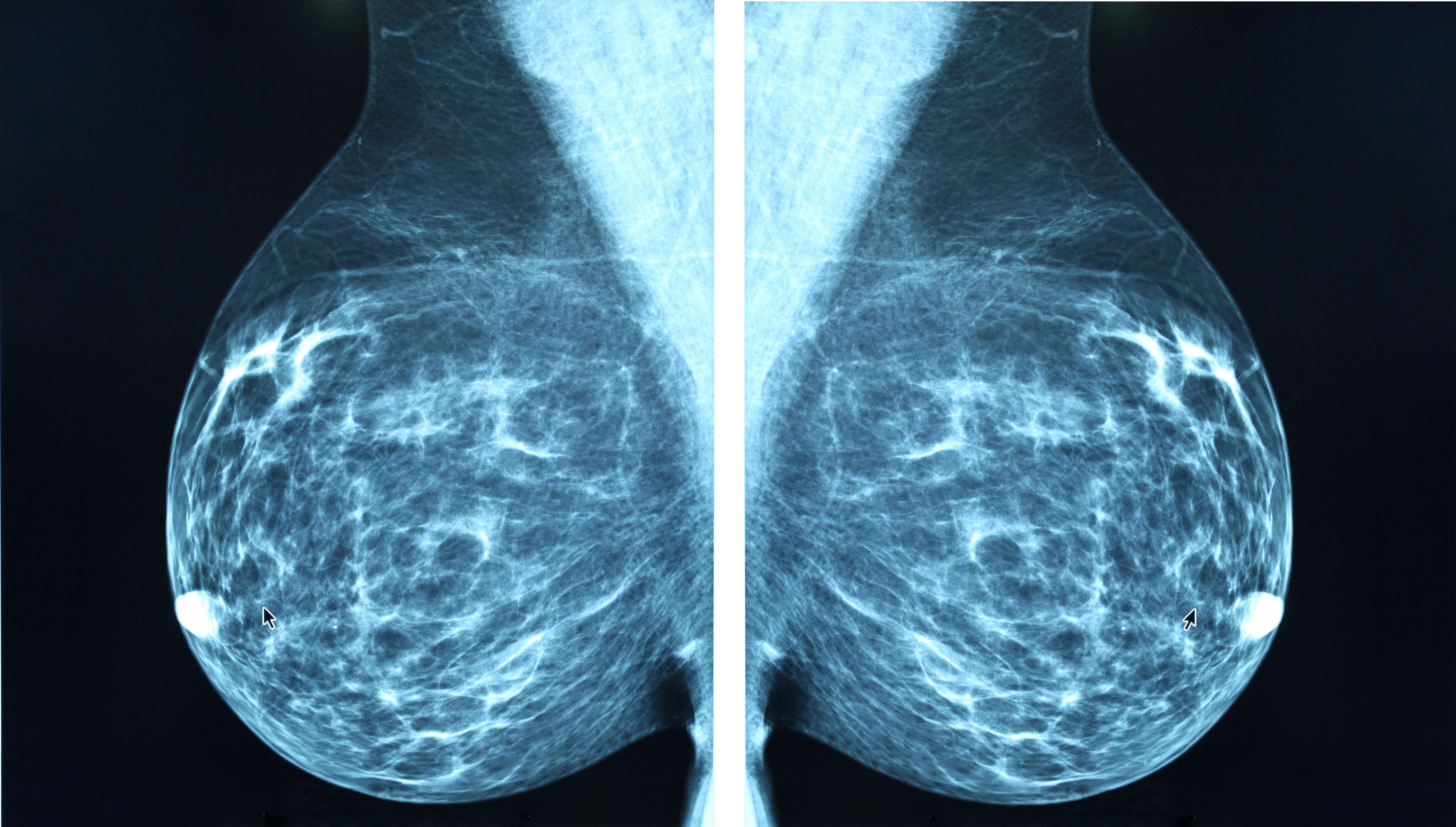
What causes breast cancer?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Who gets breast cancer?
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Breast cancer symptoms
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpg)
Types of breast cancer
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Types of invasive breast cancers
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Breast cancer treatment plan
Nov 30, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How to prevent cervical cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What is cervical cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Are there tests for early detection?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Breast cancer risk factors
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Staging and Treatment for oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How to prevent oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Risk factors of oral cancer
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What is oral cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
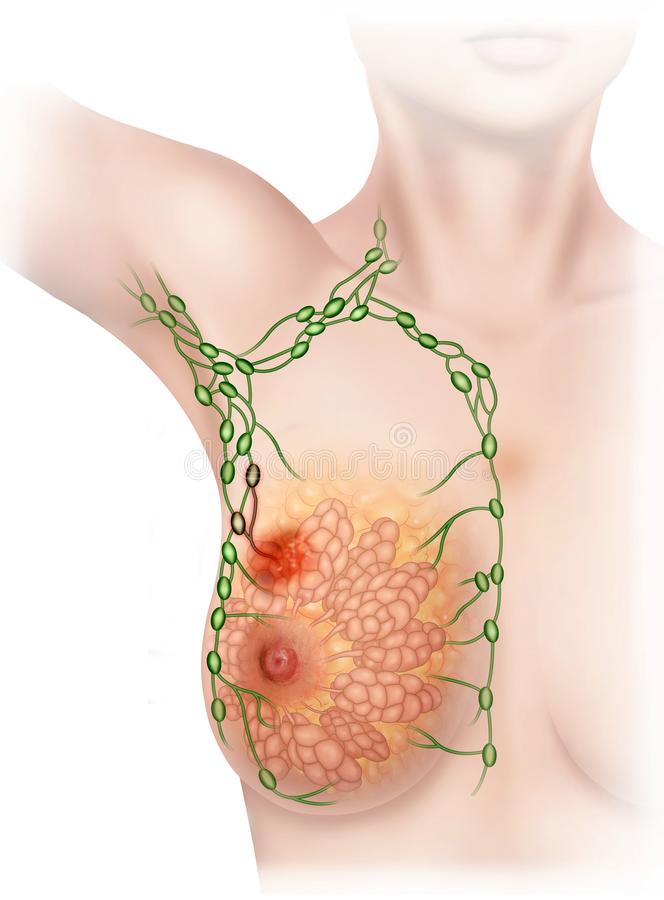
The Lymph System of the Breast
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
What Is Breast Cancer?
Nov 22, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
.jpeg)
Kidney Cancer: Myths & Reality
Nov 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
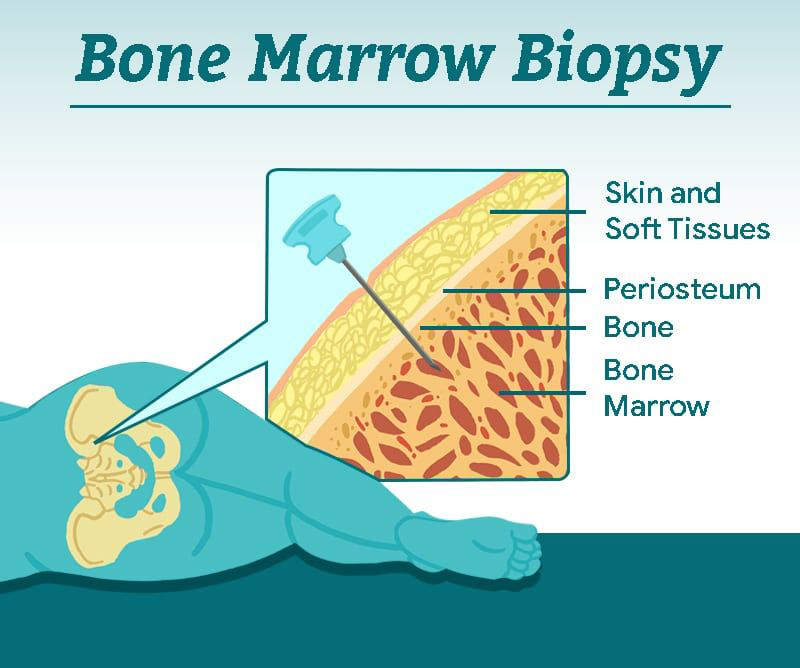
Bone marrow biopsy
Sep 29, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
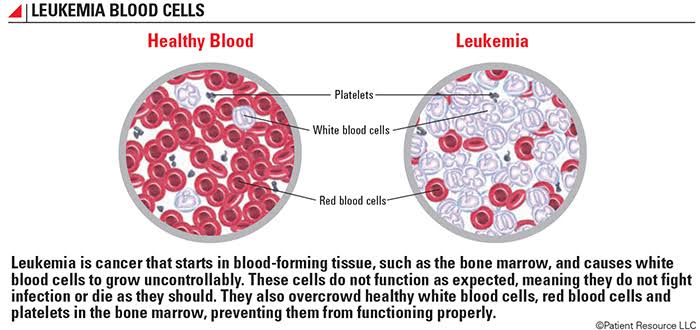
Leukemia
May 28, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
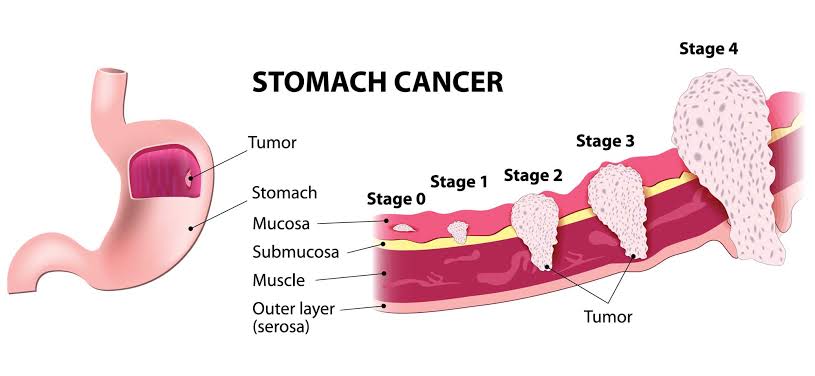
Stomach Cancer
May 28, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
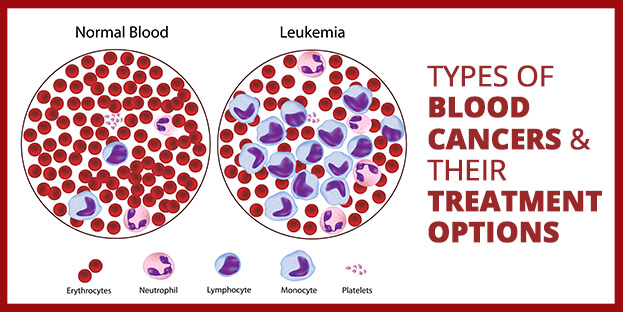
Blood Cancer – Types and Treatment
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
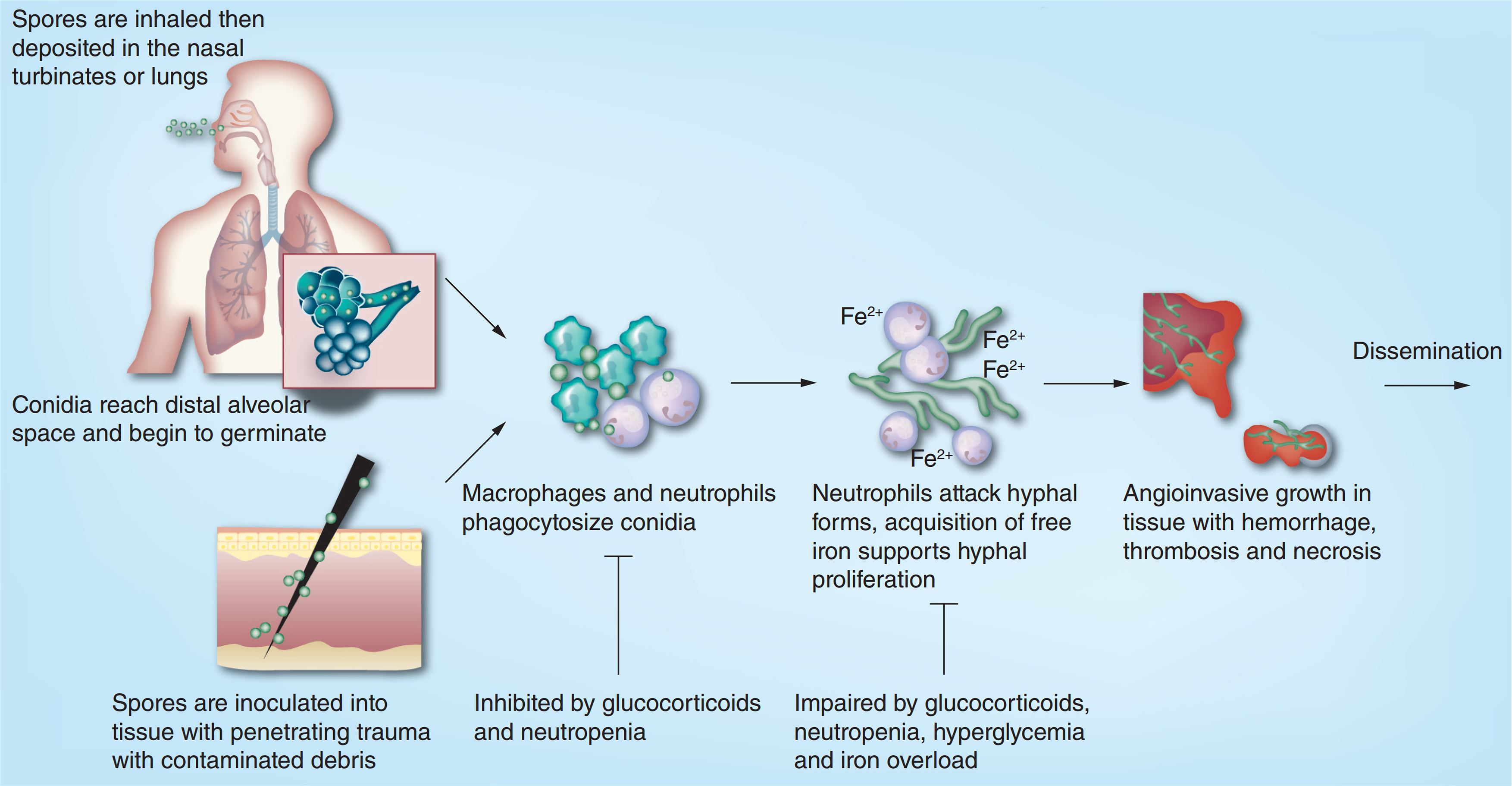
Reasons for mucormycosis in Covid-19
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
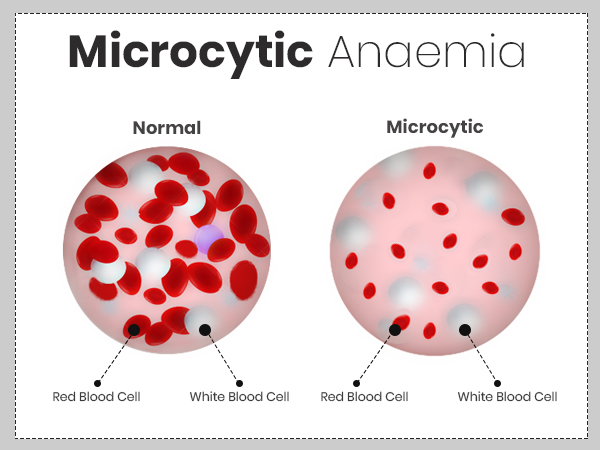
Microcytic and Hypochromic anemia is one of the common scenario we encounter in Clinics
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
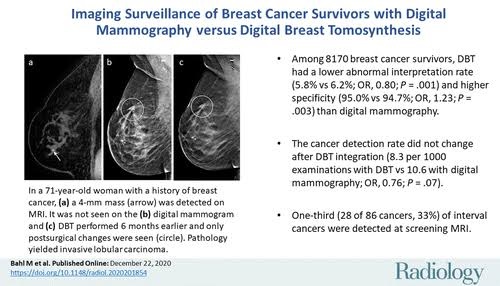
Updated Recommendations for Breast Cancer Surveillance in Young Female Cancer Survivors
May 21, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
vs
May 14, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Risk Factors of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Diagnosing lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
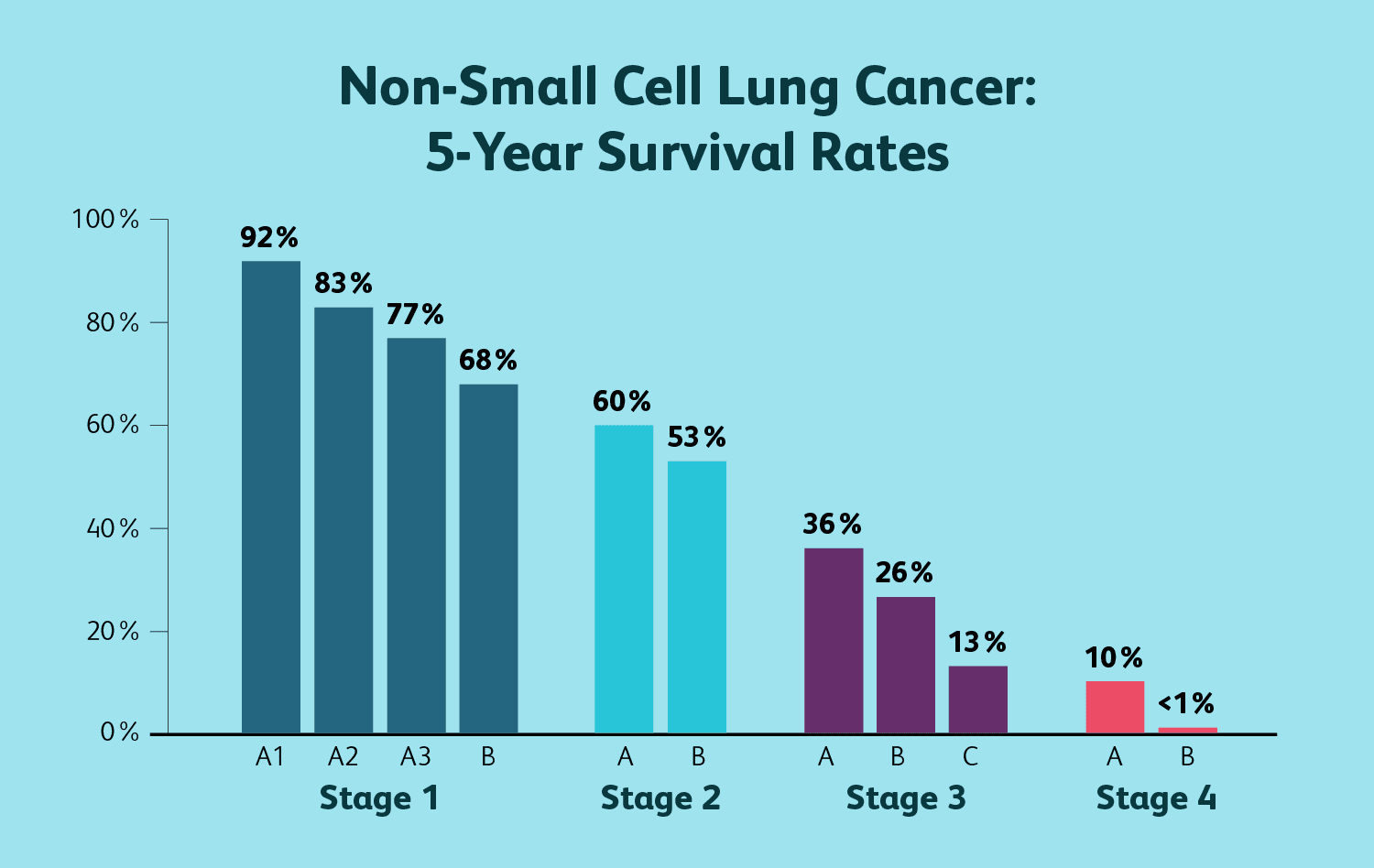
Lung cancer and life expectancy
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Home remedies for lung cancer symptoms
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
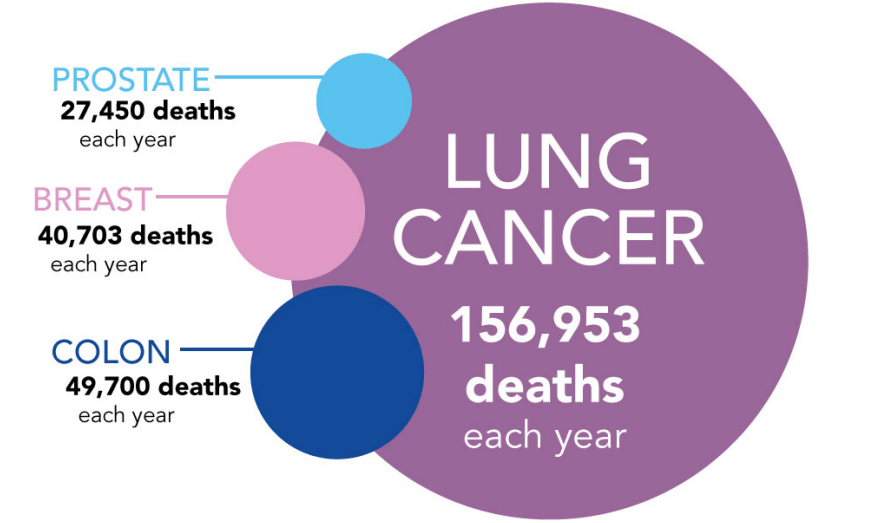
Facts and statistics about lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Diet recommendations for people with lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
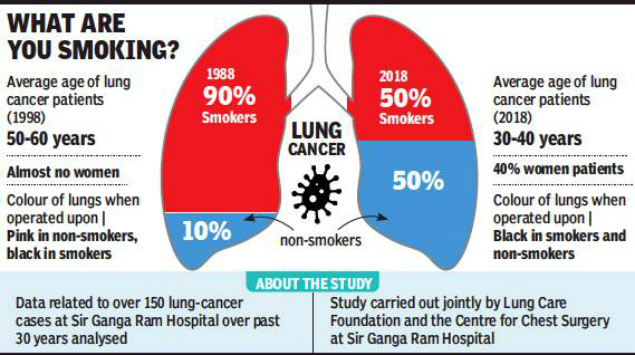
Lung cancer and smoking
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
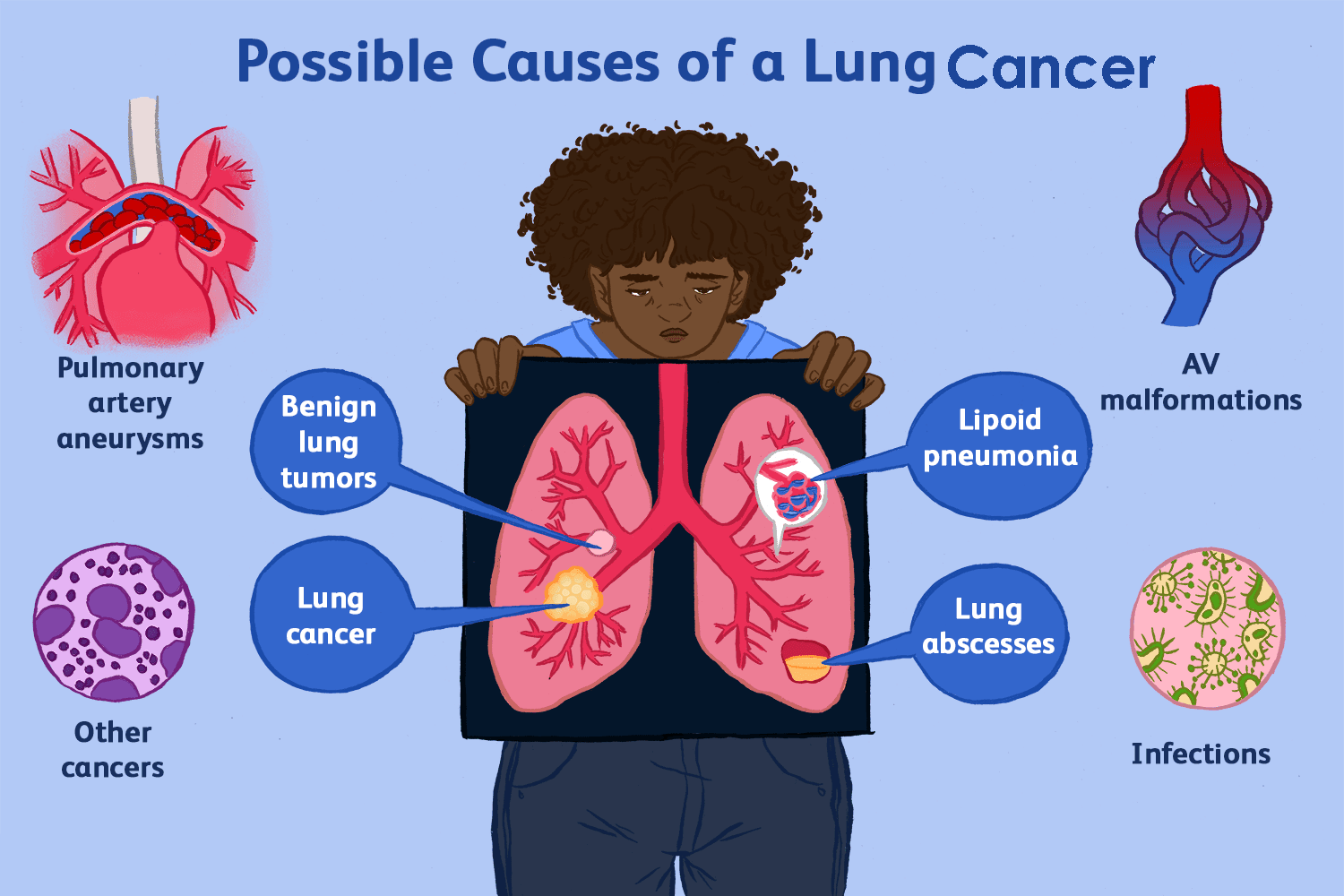
Causes of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
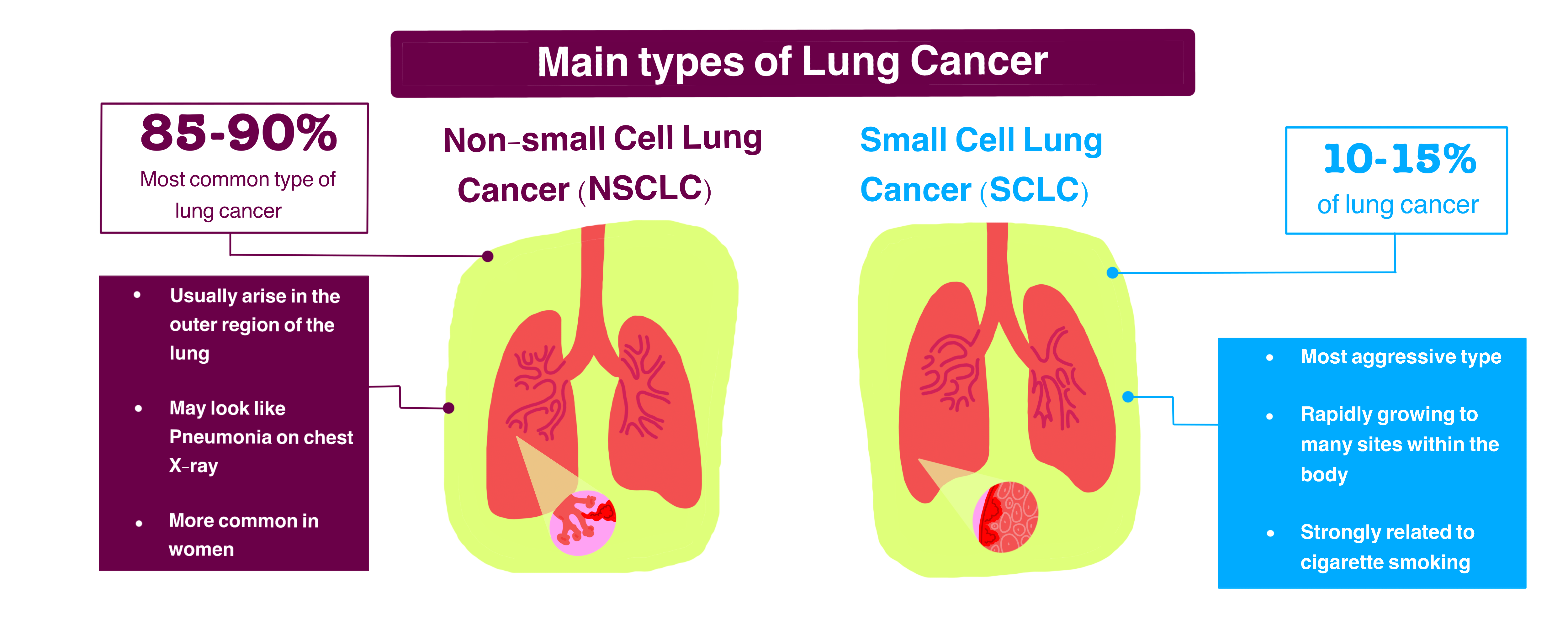
Different Types of Lung Cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Lung Cancer and its types
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
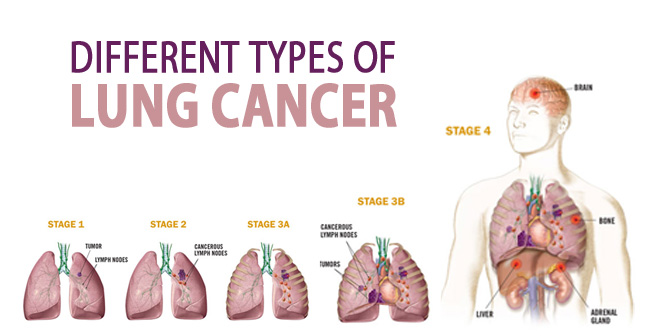
Stages of LUNG CANCER
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
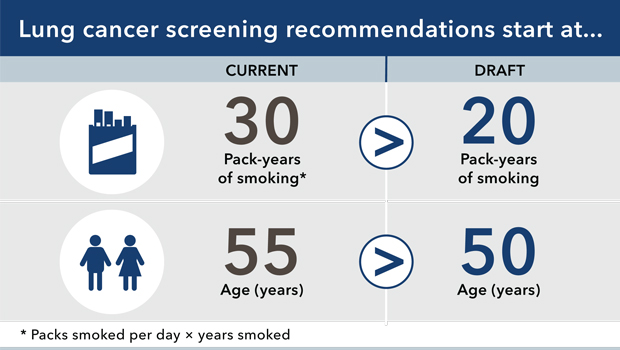
Lung Cancer and Lung Cancer Screening
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
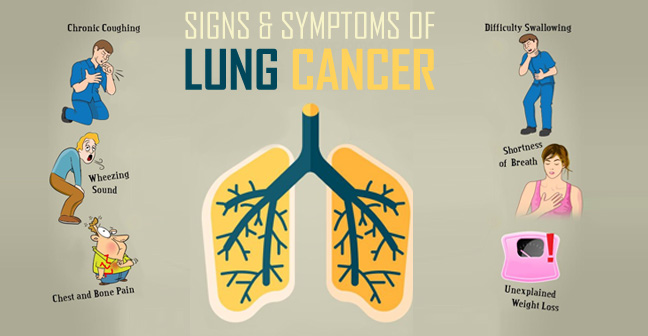
What are the symptoms of lung cancer
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
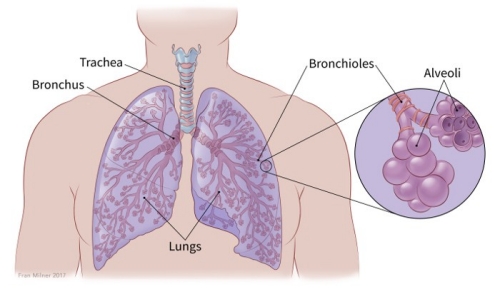
Lung cancer occurs when cells divide in the lungs uncontrollably.
Apr 06, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

KEYNOTE-365
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
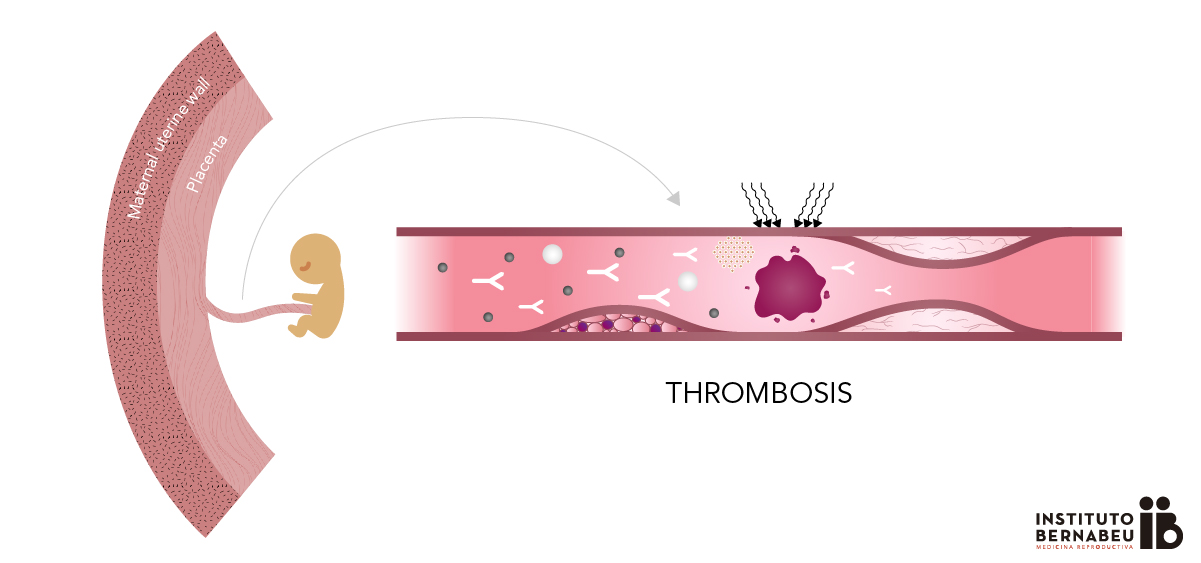
Antiphospholipid syndrome in Pregnancy
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
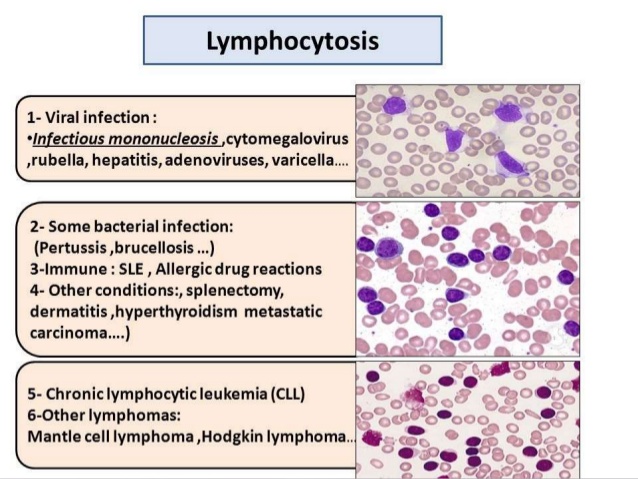
Leucocytosis
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
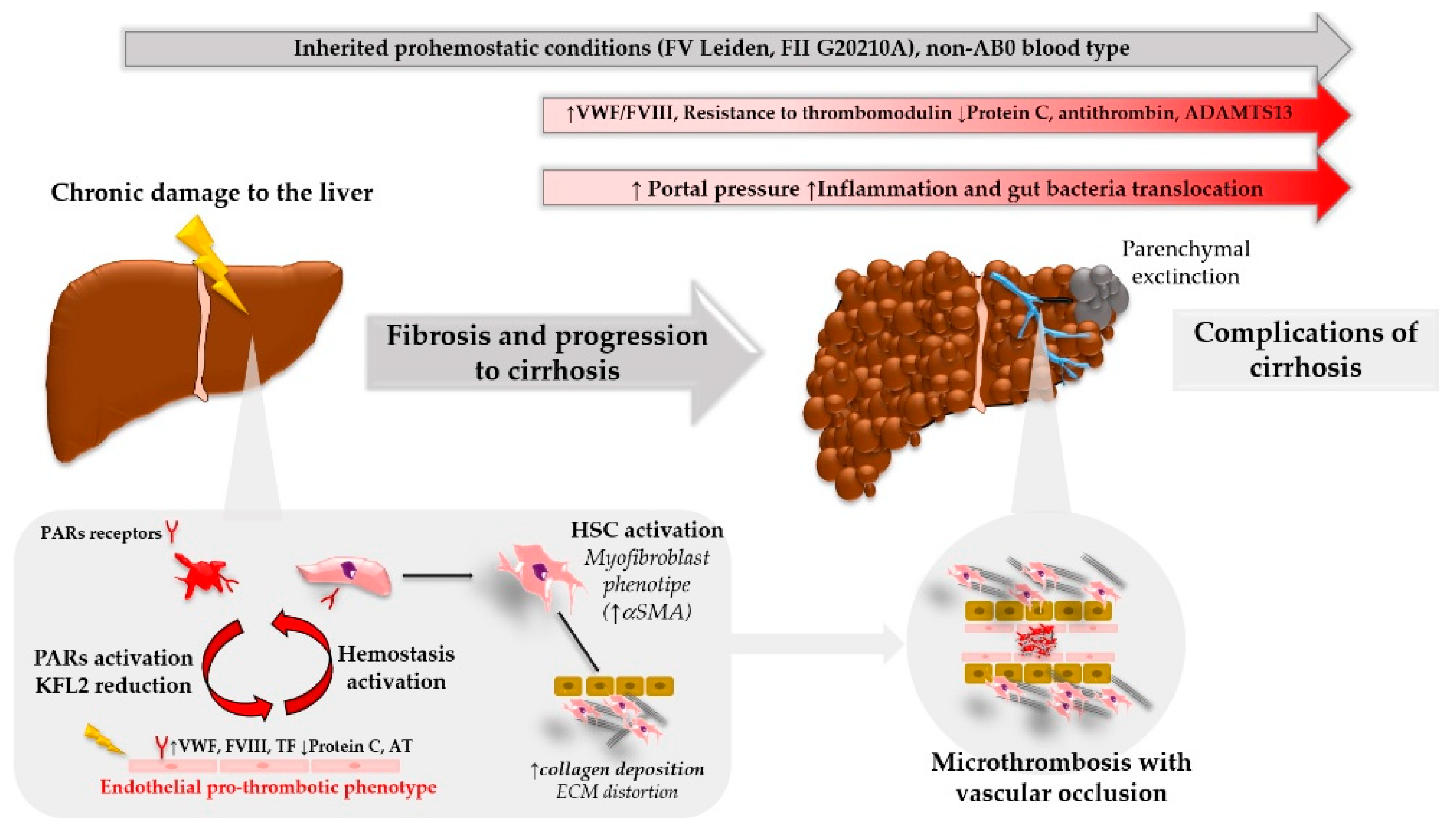
Patients with liver disease often have blood results that give an appearance of a significant bleeding risk
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
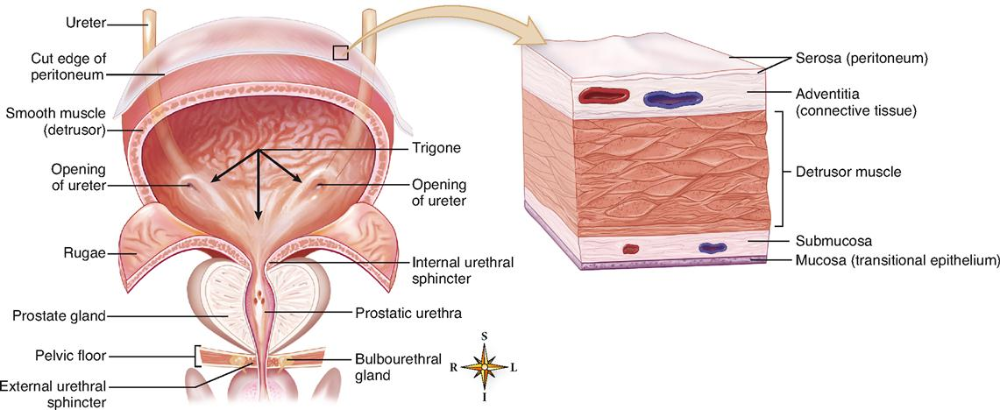
Navigating Uncertain Times in Muscle-Invasive and Advanced Bladder Cancer
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
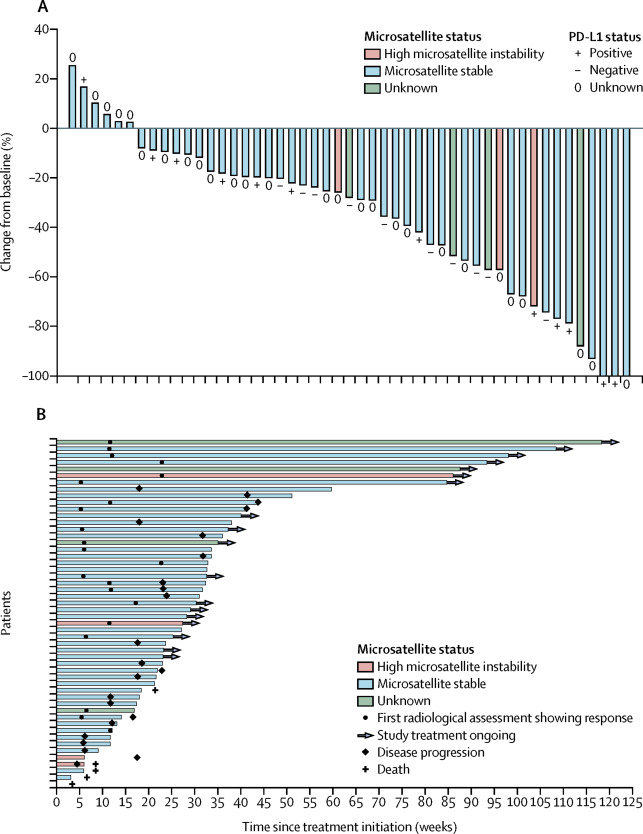
Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
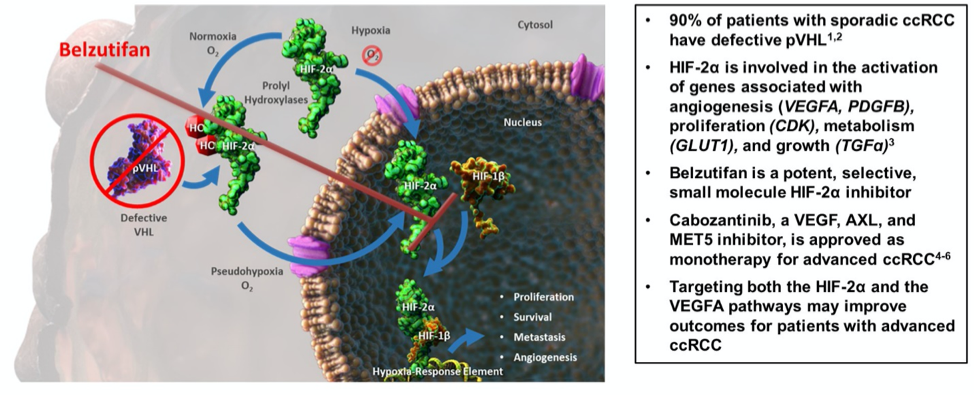
From bench to bedside, another practice-changing treatment is on the road!
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

ASH_hematology VTE guidelines in patients with cancer
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

How I Rx Newly Diagnosed Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
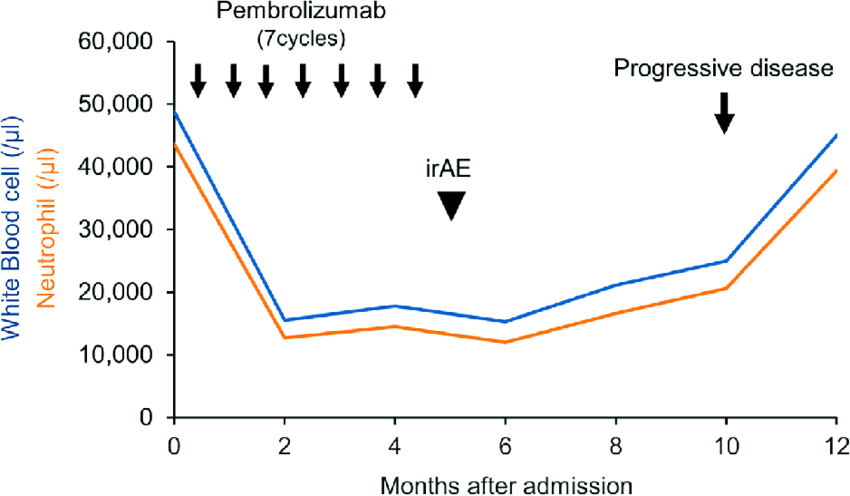
Ipilumumab plus pembrolizumab vs pembrolizumab alone in pdL1 more than 50 percentage Which is better
Mar 12, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
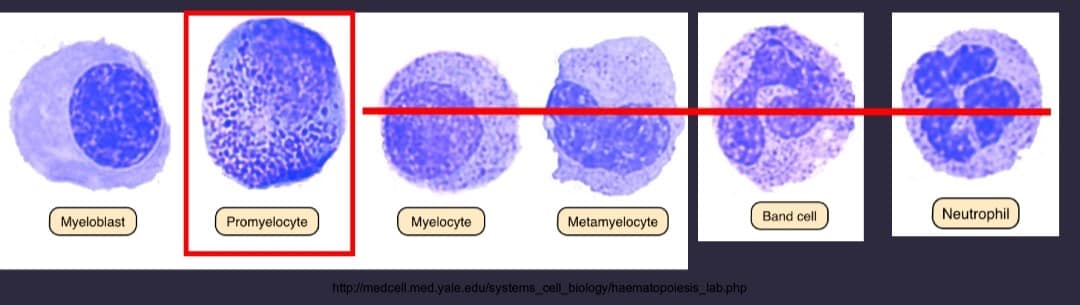
APML is medical emergency
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
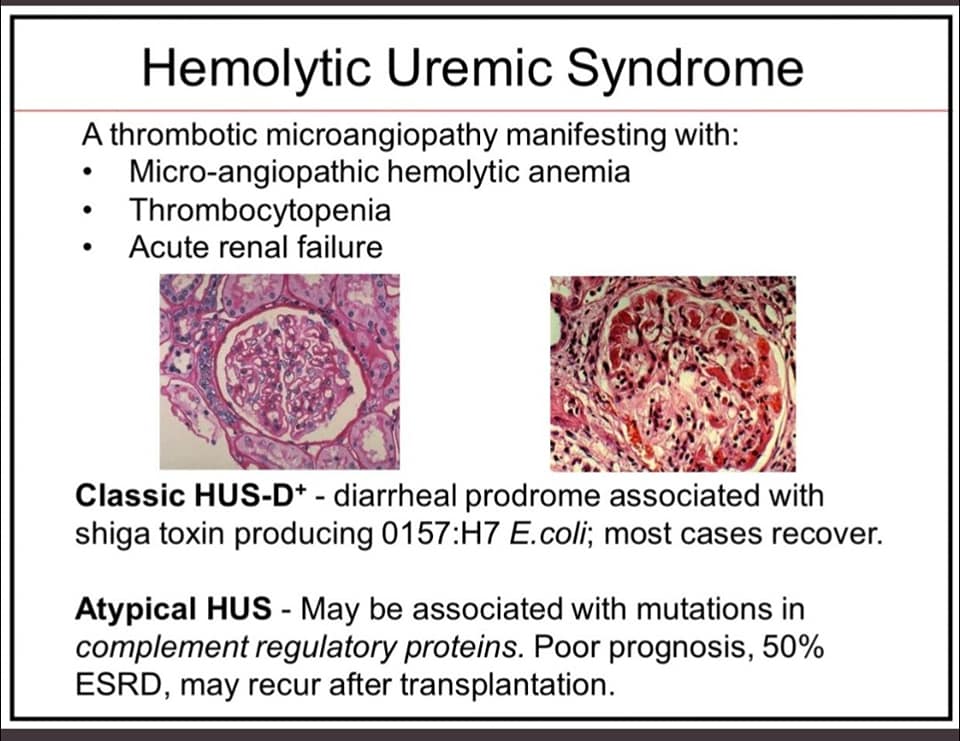
aHUS is a disease of excessive activation of the alternative complement pathway (ACP)
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
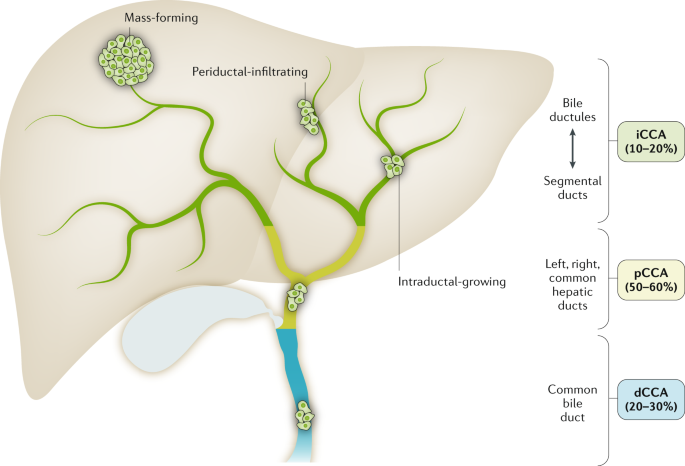
imp. point to reiterate
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
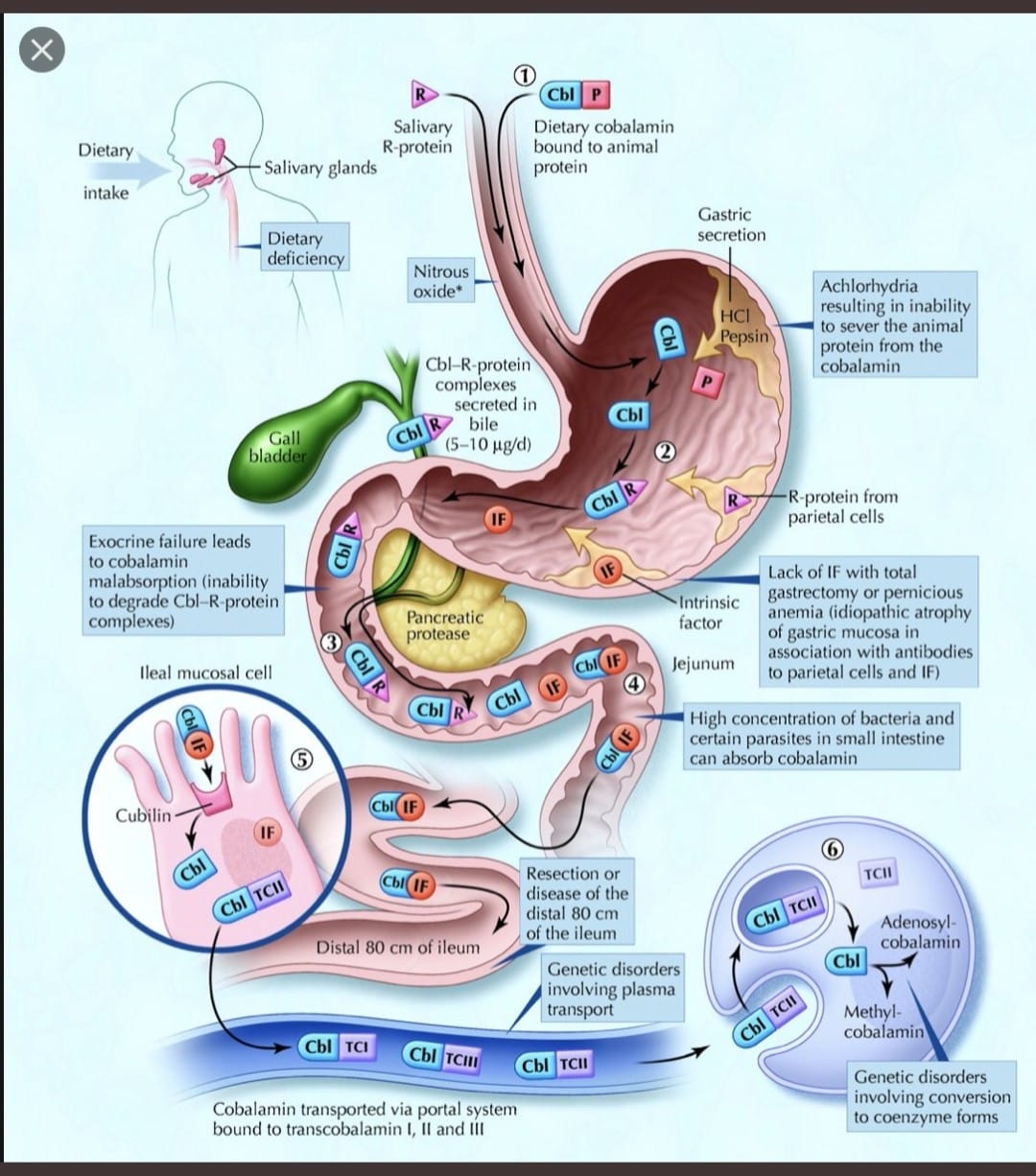
Understand B12 Absorption to Learn B12 Def
Mar 11, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
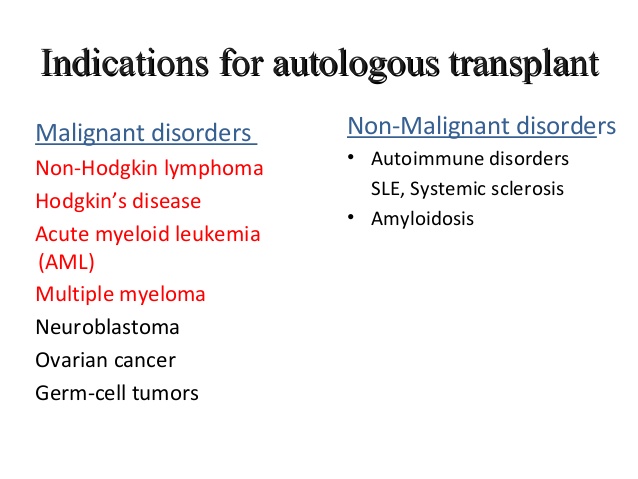
Indications for auto-transplant - for the oncology fellows
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
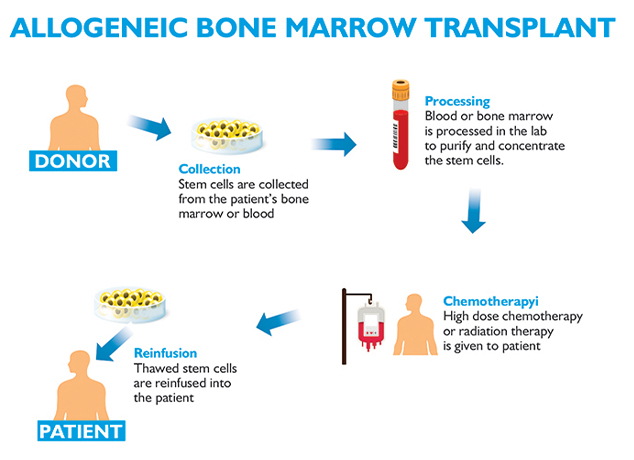
Allogeneic bone marrow transplant is the curative treatment for few relapsed leukemias and Lymphoma
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
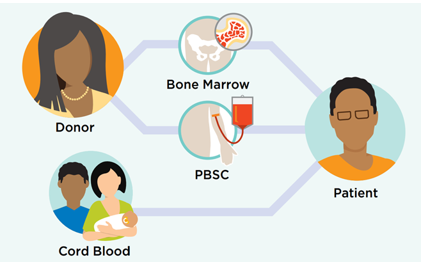
Allo BMT Basics
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
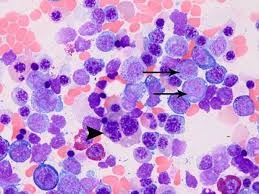
Myeloid HemePath Pearls
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Myeloid HemePath Pearls
Mar 09, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam

Amyloidosis month
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
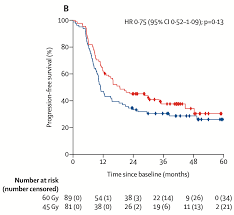
Full publication of randomized Scandinavian dose escalation trial for LS SCLC
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
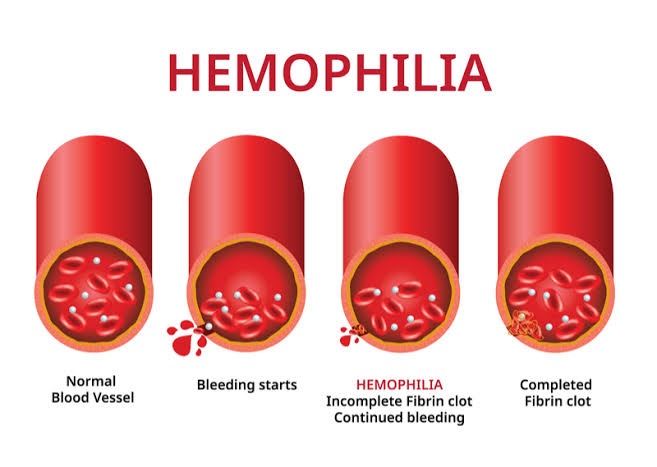
Hemophilia
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Rituximab Maintenance for Follicular lymphoma
Mar 03, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
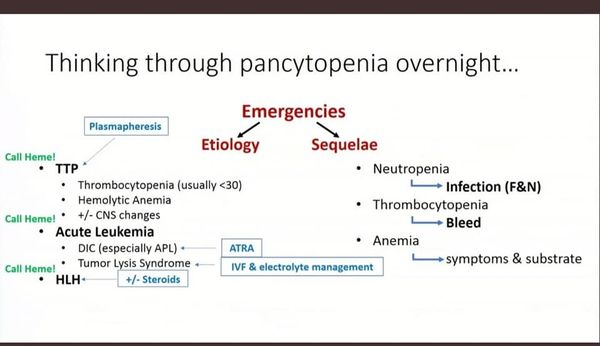
PANCYTOPENIA
Feb 23, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
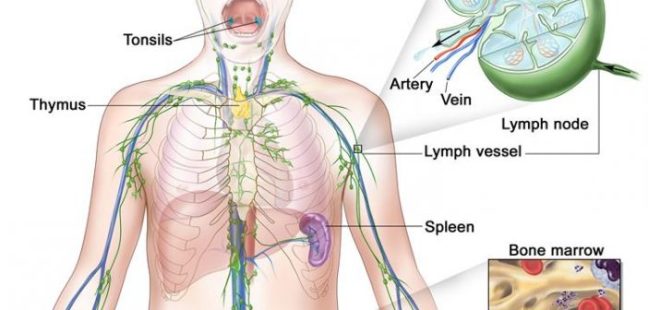
WHAT IS THE MAIN CAUSE OF LYMPHOMA?
Feb 18, 2021
Dr. Rajesh Bollam
Add a comment